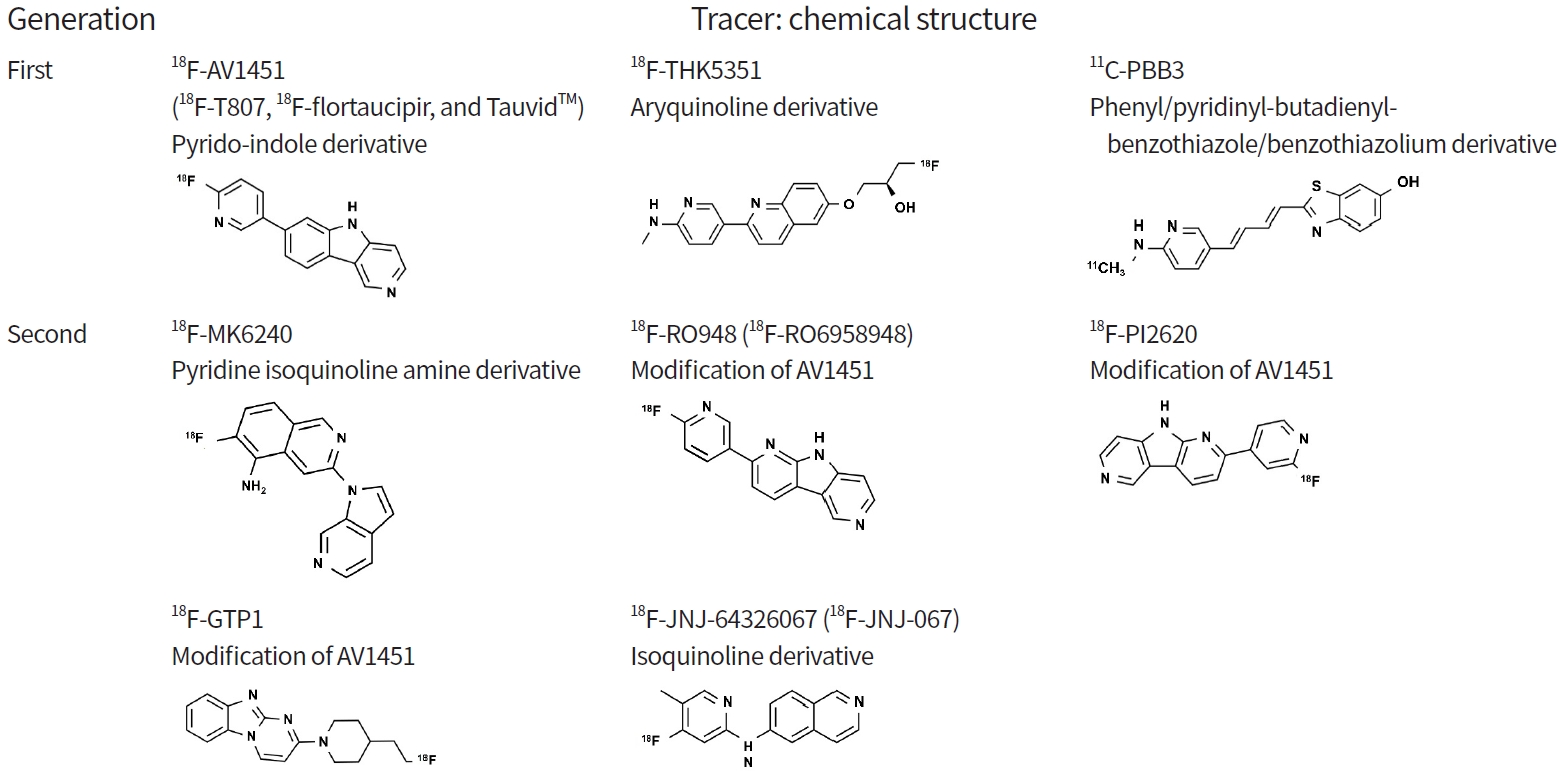
 |
 |
- Search
| Precis Future Med > Volume 7(1); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Aggregation of misfolded tau in the brain is a major pathological feature common in various neurodegenerative disorders known as tauopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal syndrome, and dementia with Lewy bodies. Tauopathies are collection of diseases with varied overlapping symptoms and complicated manifestations. Consequently, it is crucial to be able to assess tau deposits in vivo. Over the past decade, tau-specific radioligands for positron emission tomography (PET) have been developed and tested, including first-generation compounds (e.g., 18F-THK5317, 18F-THK5351, 18F-AV1451, and 11C-PBB3) and second-generation compounds (18F-MK-6240, 18F-RO-948, and 18F-PI-2620). With the recent advances of tau PET tracers, assessing the pattern of tau deposition in vivo is possible. These methods will allow accurate diagnosis of tauopathies and monitoring of disease progression. In this mini review, we summarize current findings from studies using tau PET tracers regarding neuropathological characteristics, clinical implications, and potential applications of tau PET. We also discuss methodological considerations for appropriate use of these technologies and discuss what has been learned from these findings.
Tau is a phosphoprotein encoded by the microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) gene on chromosome 17q21.3 and comprises 16 exons [1]. Alternative mRNA splicing of the MAPT gene leads to expression of six tau isoforms with three (3R) or four (4R) microtubule-binding repeats. Exclusion or inclusion of exon 10 results in either 3R or 4R, respectively [2-4]. Tau is involved in the formation and stabilization of microtubules in the nerve system, which is essential for neuronal stability and functioning. Phosphorylation of tau impacts its functionality [5]; however, hyperphosphorylation of tau causes and also increases the aggregation of tau into straight filaments, twisted ribbons, or paired helical filaments (PHFs) and, subsequently, into neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), pick bodies, glial tangles, coiled bodies, and astrocytic plaques etc. An accumulation of abnormal tau in the human brain is the main pathological hallmark of neurodegenerative disorders that are now collectively termed “tauopathies” [6,7]. Many of the most common neurodegenerative diseases are classified as tauopathies, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), Pick’s disease, and chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) [8,9], and they exhibit distinct regional distributions of abnormal tau deposition [10]. One of the main histopathological features in AD is aggregation of hyperphosphorylated tau into NFTs, along with the formation of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques [11]. The regional distribution of NFTs follows a stereotypical pattern defined as “Braak stages”: stages I–II (transentorhinal), III–IV (limbic), and V–VI (isocortical association areas) [12]. In CBD and PSP, the distinct lobar and basal ganglionic tau deposits are different from those in AD [13,14]. In addition to the distinct regional distribution of deposition, tau isoforms are an important factor of tauopathy. Tau isoforms containing either 3R or 4R are present in approximately equal distributions in the normal brain and in patients with AD, tangle predominant senile dementia, and CTE [15,16]. The ratio is substantially altered in other tauopathies: 3R isoforms are dominant in Pick’s disease and 4R isoforms are dominant in CBD, PSP, and argyrophilic grain disease [16].
Despite advances in the research of tauopathies, many questions regarding tau deposition in the pathophysiology of these neurodegenerative diseases remains unclear. These diseases have substantial biochemical and pathological similarities and show considerable overlapping clinical phenotypes [8]. Therefore, accurate and early differential diagnosis of these diseases is a clinical challenge. Because of the invention of tau tracers for positron emission tomography (PET) [17], it is possible to visualize and quantify tau pathology in the living human brain. This approach has great potential in early diagnosis, especially in cases with ambiguous clinical symptoms. In addition, tau PET imaging can be useful for subject selection and as a surrogate outcome measure in clinical trials. Since the introduction of tau PET tracers, studies using tau PET have shown an exponential increase in the field of neurodegenerative diseases (Fig. 1). Despite the potential value of tau PET imaging, however, application of this tool in clinical practice is challenging. Its value in investigating pathological tau accumulation and in diagnosing tauopathies remains to be clarified, and the development of novel tau ligands is ongoing [18]. In this brief review, we summarize and discuss findings from recent studies on various tau PET ligands and future directions of tau PET imaging.
Development of PET tracers that specifically target the tau protein in the human brain presents a great challenge [19]. In addition to the general characteristics required for an ideal brain PET tracer [20-22], the requirements for tau PET tracer are even more strict.
Low toxicity, sufficient blood-brain barrier penetration, low non-specific binding, rapid uptake and clearance from the brain, and no radiolabeled metabolites in the brain are required for brain PET tracers [23]. Furthermore, the labelling of 18F instead of 11C is preferred due to the longer half-life [23-25]. In addition, tau PET tracers have additional challenges [26]. First, tau is largely an intracellular protein and must be able to cross the cell membrane, which limits its molecular size and lipophilicity [23]. Second, tau deposits are co-localized with Aβ plaques in AD. Therefore, tracers must be selective for tau deposits over Aβ [23,24]. For example, 2-(1-{6-[(2-[fluorine-18]fluoroethyl)(methyl)amino]-2-naphthyl}-ethylidene)malononitrile (18F-FDDNP) was a promising candidate tau tracer that was originally developed for AD. However, it failed due to a lack of selectivity as it binds to both Aβ and tau [27]. The problem is that current tau PET tracers share β-sheet binding properties, but Aβ has similar structural motifs to β-sheets. In addition, Aβ is co-localized with tau deposits at much higher concentration. Tracers may bind to Aβ with different affinities [23]. Third, tau deposits in various tauopathies contain different isoform compositions: 3R and 4R tau are present in AD, tangle predominant senile dementia, and CTE; 3R tau is dominant in Pick’s disease; and 4R tau is dominant in CBD, PSP, and argyrophilic grain disease [16]. These differences hinder the selectivity of tau PET tracers in differentiating tauopathies. Due to structural similarities, the development of PET tracers that bind exclusively to specific isoforms remains challenging.
A variety of molecules has been suggested and tested for tau imaging. Several tracers are now available in different stages of clinical development, which can roughly be categorized into first-generation and second-generation tau PET tracers.
First-generation tau PET tracers can be divided into three families according to chemical structure [23,30,31]: pyrido-indole derivative ligands (18F-AV680 and 18F-AV1451) [32,33]; aryquinoline derivative ligands (THK family: 18F-THK523, 18F-THK5105, 18F-THK5117, 18F-THK5351) [34-37]; and phenyl/pyridinyl-butadienyl-benzothiazole/benzothiazolium derivative ligands (11C-PBB3) [38-40].
18F-AV680 (formerly 18F-T808) and 18F-AV1451 (formerly 18F-T807, 18F-flortaucipir, and TauvidTM [Eli Lilly and Co.]) were developed by Siemens and are now owned by Eli Lilly. 18F-AV1451 showed better properties as a tau imaging agent [17,41] and became the most widely applied tracer. It was recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for clinical use in the United States as TauvidTM (Eli Lilly and Co.) [42]. To date, 18F-AV1451 is the first and only FDA-approved tau PET imaging agent. The THK family (18F-THK523, 18F-THK5105, 18F-THK5117, 18F-THK5351) was developed at Tohoku University in Japan [25,34,36,37,43]. Among the tracers, 18F-THK5351, the newest derivative in this family, exhibits better characteristics including a higher signal-to-noise ratio and lower white matter (WM) retention. However, the first three of these tracers have been precluded from the next stages of clinical development due to high retention in WM [44]. 11C-PBB3 (Chiba, Japan), which is derived from the same tracer family as the Aβ ligand Pittsburgh Compound B (PIB), has been used to image AD and non-AD tauopathies [38,39]. However, it exhibited low specific binding and radio-labelled metabolites capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier [45].
Despite the initial success of first-generation tau tracers, they exhibit some drawbacks, including low specific binding, off-target binding, and radiolabeled metabolites entering the brain. Off-target binding is a critical flaw as a specific tau PET tracer (see section of ‘off-target binding’). Given that 18F-AV1451 is a currently established and approved tau PET tracer, we focus on this tracer.
It is crucial to verify that the PET tracer signal detected in vivo corresponds to pathology. For this purpose, autoradiography studies on postmortem brain tissue have been performed to assess the role of tau PET tracer signal. Most first-generation tracers bind to the tau aggregates formed in AD (AD tauopathy, a mix of 3R/4R tau isoforms) [46-48]. However, they exhibit lower affinity for the 3R or 4R isoforms that characterize many non-AD tauopathies and may be related to the lower tau aggregate densities that hinder detection using tau PET [4].
Supporting 18F-AV1451 as the most established tau PET tracer, extensive studies have validated neuropathologic correlation of tau PET [49-53]. A large end-of-life study [49] and extended case series [50,51] demonstrated that 18F-AV1451 more accurately detects AD tauopathy in individuals in more advanced Braak stages (i.e., Braak >IV; the accuracy for detecting tau deposit corresponding to Braak stages V and VI was 87.5% [95% confidence interval, 77.2% to 93.5%] [49]). There is a strong correlation (R2 range, 0.66 to 0.76) between tau PET level and quantitative neuropathologic tau burden in corresponding brain regions [52,53]. In addition, in MAPT mutation carriers with mixed 3R/4R tau pathology, similar to AD, there is a strong correlation (R2=0.86) between the tau PET signal and the postmortem neuropathologic tau burden [54,55].
Unlike AD tauopathy, the evidence supporting the in vivo correspondence of PET signal to tau aggregation in non-AD tauopathies is less clear. Studies on non-AD tauopathies have shown mixed results. For 18F-AV1451, while studies have reported differences of detected in vivo PET signal between controls and individuals clinically diagnosed with 4R tauopathies (PSP, CBD) are part of non-AD tauopathies [55-60], binding to non-AD tauopathies has been limited to postmortem studies [4,50,61].
Studies showed that 18F-AV1451 binds to motor-related subcortical gray and WM structures in patients with corticobasal syndrome, which distinguishes patients from controls [55-57]. However, only a few autopsy-confirmed cases were reported with either moderate-to-strong correlation (R2 range, 0.59 to 0.79) [62,63] or a limited correlation of PET signal with tau pathology [50].
There are significant differences of tracer retention between controls and clinically diagnosed PSP patients in studies using 18F-AV1451 PET scan [55,58-60]. Tracer retention is predominant in the substantia nigra and basal ganglia, which also show off-target binding to 18F-AV1451, complicating interpretation [4]. There was no significant correlation between cortical 18F-AV1451 PET signal and neuropathologic 4R tau [61], and little binding outside the off-target regions was observed [50]. The number of autopsy-confirmed cases was too small to draw any conclusions [50,61,64].
In summary, the currently established first-generation PET tracer binds to AD tauopathy in the more advanced Braak stages (>IV). However, the diagnostic value of the tracer for AD tauopathy may be suboptimal. NFTs may be present at levels suitable for a neuropathological diagnosis of AD, Braak staging II tau pathology in the presence of at least moderate levels of cortical amyloid pathology, even in patients with a negative 18F-AV1451 scan. Besides, the potential of the tracer in quantifying and visualizing non-AD tauopathies in vivo is highly limited since tracer binding in most non-AD tauopathies is weak and overlaps to a large extent with known off-target binding regions [4].
Quantification of tau retention in the brain is of great interest in the clinical applicability of tau PET imaging. Therefore, determination of an optimal method for quantifying tau deposit is essential [45,65-69]. In vivo kinetic models using arterial sampling are the “gold standard” for accurate assessment of the pharmacokinetic properties of tau PET tracers. Kinetic modeling with arterial sampling in humans has been performed for first-generation tracers [45,67,68,70,71], except 18F-THK5351. However, finding and optimizing a less invasive and less laborious method that can be easily implemented in the clinic is of great value. In this regard, several studies on less invasive quantification methods, using reference tissue models without arterial sampling, have been performed. Studies have also examined the optimal time interval for quantification and validated semi-quantitative quantification approaches such as standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR) [3]. All tracers showed the feasibility of using reference tissue models and SUVR values as a reliable measurement of tau deposit in vivo. A previous study has reported good correlations between SUVR and plasma-input kinetic model-derived parameters [71], which has a great value for future applicability, since these methods are more suited for use in clinical settings. Cerebellar regions were selected as the reference tissue in all such models because they are relatively spared from tau deposits in AD until late in the disease course [3,12].
First-generation PET tracers show off-target binding to such an extent that it impedes the specificity of these tracers to detect tau pathology. Sources of off-target binding vary widely and include monoamine oxidase (MAO), amyloid deposit, calcifications, iron, and microhemorrhages [31,72].
11C-PBB3 and the 18F-THK ligands show substantial off-target binding to amyloid deposits and MAO-B, which limits the use of these traces for selective tau pathology detection [31,73,74]. 18F-AV1451 shows off-target binding at the substantia nigra, eye, basal ganglia, longitudinal sinuses, pituitary, and choroid plexus (Fig. 2) [47,75,76]. The most apparent targets are neuromelanin in the substantia nigra and retinal pigment epithelium in the eye [47]. MAO is also a potential source of off-targeting, as shown in in vitro study of 3H-AV1451 binding to MAO-A and MAO-B [77]. However, in vivo studies using 18F-AV1451, MAO does not appear to be a significant binding target [78,79]. Interestingly, 18F-AV1451 also shows elevated tau PET signal in patients with clinical syndromes typically associated with TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) type C rather than tau pathology, such as the semantic variant of primary progressive aphasia [80,81].
As a result of continued efforts to minimize the off-target binding observed in first-generation tau PET tracers, second-generation tracers, including 18F-MK6240, 18F-RO948 (18F-RO6958948), 18F-PI2620, 18F-genentech tau probe 1 (GTP1), and 18F-JNJ-64326067 [82-87], are now available. Many potential tracers are being developed and analyzed for use as biomarkers. In this review, we focus on several tracers that have passed the initial validation stage for clinical use.
18F-MK6240 is a pyridine isoquinoline amine derivative that was developed by Merck. This tracer shows good characteristics for in vivo imaging, including an appropriate dynamic SUVR range, desirable kinetics, significant binding in regions known to contain AD tauopathy, and correlation with clinical endpoints [88].
18F-RO948 and 18F-PI2620 are derivatives of 18F-AV1451, with a pyrido-indole-based structure. They can distinguish AD subjects from healthy controls and have promising characteristics as tau PET tracers [18,42]. 18F-RO948, developed by Roche [18,42], exhibits significantly higher tracer retention in patients with AD compared with controls, lack of radiolabeled metabolites entering the brain, and no defluorination [42,89]. 18F-PI2620, developed by Piramal Imaging, has robust uptake and fast wash-out in AD subjects and focal asymmetric uptake in AD tau-bearing areas. Importantly, preclinical characterization of 18F-PI2620 has shown strong binding in Pick’s (3R) and PSP (4R) non-AD tauopathies [90].
18F-GTP1, developed by Genentech, is under evaluation in a longitudinal natural history study. Preliminary cross-sectional results show an association between 18F-GTP1 uptake and cognitive deficits in AD but also notable off-target binding in the basal ganglia [91].
While first-generation tracers have shown lower affinity for the 3R or 4R isoforms of tau that characterize non-AD tau pathology [18,46-48,86], for some of the second-generation tracers, there is evidence of binding to the 3R or 4R isoforms from autoradiography studies [92,93]. This neuropathological correlation could facilitate more reliable diagnosis of non-AD tauopathies by tau PET imaging. In addition, these tracers show promising binding profiles with lower off-target binding in the target regions for PSP or multiple system atrophy compared with first-generation tracers [75,76]. 18F-PI2620 has the capability of binding to the 4R isoform in tissue of individuals with PSP [92]. A multicenter study reported significantly increased 18F-PI2620 binding in predefined PSP target regions in clinically diagnosed PSP patients, indicating the value of this tracer in differentiating suspected patients with PSP [92]. However, despite some evidence of binding to 4R tau pathology on autoradiography [92], a recent study showed limited binding of 18F-PI2620 to 4R tau pathology [94]. Notably, the in vivo second-generation tau PET signal only partially reflects 3R or 4R tau pathology. More data are needed to validate each of these tracers as an in vivo imaging biomarker of tauopathy.
The off-target binding profiles of second-generation tracers still vary but to a lesser degree and extent compared with first-generation tracers. The most apparent off-target binding target of 18F-MK6240 is neuromelanin in the substantia nigra and retinal pigment epithelium [86]. In addition, as a derivative of 18F-AV1451, 18F-RO948 is associated with binding to neuromelanin, like its predecessor [4,18]. In head-to-head studies against 18F-AV1451, 18F-MK6240 and 18F-RO948 show reduced binding to the basal ganglia, longitudinal sinuses, pituitary, and choroid plexus [4,75,76]. In contrast, they show substantial off-target binding to the meninges and skull, especially in women [4,95,96]. Off-target binding profiles of 18F-PI2620 show involvement in the meninges, skull, and venous sinuses [94]. Details of tracers are summarized in Table 1 [18,23,33,43,45-47,77,82,89-91,95,97-106] and Fig. 3.
Because of considerable overlap of clinicopathological features across neurodegenerative disorders related with tauopathy, diagnosis and differentiation of the diseases are challenging. In secondary tauopathies such as AD, tau pathology is considered a response to other pathological events like Aβ [107,108]. In primary tauopathies such as PSP and CBD, abnormal aggregation of tau is the major hallmark of the pathology. With the emergence of tau PET imaging, diagnosis of tauopathies has received increasing attention. Given that most neurodegenerative dementias, including AD, are characterized by tauopathy, tau PET imaging may be able to detect many dementias in a diagnostic setting [109]. Furthermore, tau PET tracers, such as 18F-AV-1451, 18F-MK6240, 11C-PBB3, and 18F-RO948, showed substantial diagnostic performance for distinguishing AD dementia from non-AD neurodegenerative disorders, with high sensitivity and specificity [40,110-112]. However, although tau PET imaging has the potential to discriminate AD dementia patients from cognitively normal (CN) individuals, the individual diagnostic value of tau PET in the clinic has not been fully assessed. In a recent study, tau PET showed a similar impact on diagnostic confidence to amyloid PET. However, negative tau PET showed a lesser impact on etiological diagnosis compared with negative amyloid PET [113].
Of note, there is a strong relationship between the symptomatology of AD and the pattern of tau PET deposition. Retention of tau PET tracer is prominent in the clinically affected regions of clinical variants of sporadic AD, such as posterior cortical atrophy, logopenic variant of primary progressive aphasia, or behavioral/dysexecutive variant [114-116]. Therefore, tau PET imaging can be useful in accurately detecting atypical variants of AD, which show highly distinct patterns compared with typical AD [114,117]. There is also a correspondence between retention of tau PET tracer and autosomal dominant AD, a subgroup of AD that is estimated to account for approximately 1% of AD cases [118]. Tau deposits were associated with symptom onset, and the regional binding pattern was different from that of non-autosomal dominant AD [119]. Given its high specificity, tau PET may be useful to discriminate stages of AD, including preclinical, prodromal, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and dementia (Fig. 4) [3,120]. While amyloid PET is likely not sufficient to discriminate between symptomatic stages of AD, the intensity and spatial pattern of tau PET tracer retention have the potential for such discrimination [3,121,122]. However, previous studies have demonstrated substantially decreased discriminative accuracy of tau PET at the prodromal stage of AD compared with more advanced stages [101,123,124]. Therefore, more data are needed to draw conclusions.
Although the presence of Aβ deposit is considered necessary for a diagnosis of AD, such deposits are prevalent among the elderly [125]. Furthermore, individuals with amyloid positivity can remain in a cognitively unimpaired state for decades before they experience cognitive decline [125,126]. Amyloid PET seems to be a suboptimal predictor of clinical progression in cognitively unimpaired individuals. However, tau PET has been found to have great value in predicting preclinical and prodromal cognitive changes [127]. Interestingly, in a longitudinal study with 129 cognitively unimpaired participants who underwent amyloid and tau PET scans and were followed for a minimum of 2 years, the amyloid-positive and tau-positive subjects showed cognitive decline over the course of follow-up, whereas both amyloid-negative/tau-negative subjects and amyloid-positive/tau-negative subjects remained cognitively unimpaired. Only one subject classified as amyloid-negative and tau-positive was cognitively unstable. Both tau and amyloid showed an association with cognitive decline; however, only tau remained significant when both variables were included in the analysis. This result supports the notion that cognitive decline is predominantly driven by tau pathology and consistent with observations that tau deposition in the neocortex manifests as the disease progresses [127,128]. Tau PET is superior to amyloid PET in predicting preclinical and prodromal cognitive changes [127].
Tau PET has great potential as a prognostic marker in symptomatic stages of AD. The intensity of amyloid and tau PET level at baseline scan are strongly associated with more rapid cognitive decline [129,130]. Positivity on 18F-AV1451 PET scan was a strong indicator of future cognitive decline in patients with MCI and AD [131]. Notably, the specific distribution of baseline tau PET deposit was predictive for future brain atrophy even at the single-patient level among those with MCI and AD and was particularly strong in younger patients [132].
In summary, tau PET may be useful to detect atypical variants and to discriminate stages of AD. The retention of tau PET tracer is a prognostic marker in the prodromal stage as well as in the symptomatic stage. Tau PET positivity, especially in combination with amyloid PET positivity, is an excellent biomarker in predicting short-term progression of cognitive decline in individuals with risk of AD, which supports the notion that tau pathology is a key driver of cognitive decline [127,128,132]. Tau PET may be potentially used for individualized risk profiling and state assessment in clinical practice.
Neurodegenerative disorders that are primary tauopathies have distinct patterns of spatial distribution of tau deposits, allowing differentiation of tauopathies by tau PET imaging. Imaging of the regional distribution of tau pathology may be useful in distinguishing diseases classified as non-AD tauopathy such as CBD, PSP, and primary age-related tauopathy (PART).
Tau PET may be helpful in diagnosing CBD and PSP, which are types of atypical parkinsonism and have substantial clinicopathological overlap. These diseases are characterized by deposition of abnormally hyperphosphorylated tau predominantly in subcortical regions, in contrast to AD [13,14]. Concordance between retention of tau tracer in PET imaging and pathological patterns of tau deposition was reported in patients with PSP and CBD. In patients with a clinical diagnosis of PSP, high retention of tau PET tracers was reported in the basal ganglia, thalamus, midbrain, and cerebellum; this is consistent with the areas expected based on previous neuropathological studies [58-60,133,134]. In Aβ-negative patients with clinical diagnoses in the CBD spectrum, tau PET tracers 11C-PBB3, 18F-THK5317, and 18F-THK5351 were predominantly located in WM and the basal ganglia [82,133,135]. 18F-RO948 PET also can visualize representative patterns across diagnosis groups including CBD, PSP, and AD [4]. Importantly, tau PET may be superior to other AD biomarkers, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and most biofluid markers, in regard to early and reliable diagnosis [110,123,136,137].
Tau PET also has the potential utility for differential diagnosis between dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and AD. DLB is characterized by α-synuclein aggregates, known as Lewy bodies. However, tau deposits similar to those in AD pathology are also common, and clinical distinction between DLB and AD can be challenging [138-140]. 18F-AV 1451 retention in patients with DLB was higher than that in controls but varied widely [141]. In addition, the probable DLB patient group showed lesser 18F-AV 1451 retention than the probable AD group, and retention in medial temporal lobe was highly distinctive, which allows researchers to distinguish AD from probable DLB [142].
PART is a pathologic diagnosis that shows NFTs (Braak stage ≤4) with low, if any, amyloid burden [143] and is attracting attention with development of tau PET. PART was thought to represent the equivalent of the previously described “suspected non-Alzheimer’s pathophysiology” (SNAP), but this is debatable [144]. Investigations using tau PET supported the hypothesis that SNAP is the in vivo counterpart of PART. Studies have described cases possibly representative of PART, Aβ-negative cases in CN individuals with focally elevated cortical tau PET tracer retention [4,145-147]. However, another study reported contrasting findings. In that study, CN individuals with SNAP did not exhibit evidence of elevated tau, which suggests that this biomarker construct does not represent amyloid-independent tauopathy [148].
Together, these findings support the potential of tau PET tracers for differentiating non-AD tauopathies. However, some tau PET tracers might bind to non-target molecules and might not bind to substantially to tau pathology [46,47]. The tracers experience varying degrees of off-target binding at various locations including the substantia nigra and basal ganglia, which hinders the specificity of these tracers to detect tau pathology and can limit the diagnostic performance for tauopathies. In addition, the current diagnostic utility of tau PET in diagnosing individual patients is unclear. Thus, further investigation for each tracer is needed to assess the value of tau PET for non-AD tauopathies.
Tau retention status in vivo imaging has been assessed using quantitative thresholds or visual assessment and usually is reported as binary classification [4,149-151]. The results are significantly influenced by the methodologies for classification of PET images [150] and require proper selection of brain regions in which positivity will be determined [151]. However, there is no established methodologic approach, which limits comparisons between studies. Given that the tau PET signal is substantially affected by factors including tau isoforms, off-target binding, and disease stage, the definition of tau PET positivity requires further study.
Disease stage is important and influences the region selection for classification, especially in AD. Regions of the temporal lobe cortex are candidates for positivity in the early stage of AD and the temporoparietal cortex is a candidate for positivity in later stages of the disease [4]. In cases with low accumulation of tau, the PET signal is not as easily distinguished from background noise. Consequently, the positivity of tau PET may be more affected by region selection in early stages of the disease. At the preclinical disease stage, the entorhinal or transentorhinal cortex has been proposed as a potential reference region (RR) to define tau PET positivity since it is typically the first region in which tau PET tracers can detect tau accumulation [4]. However, autopsy studies have reported that entorhinal tau deposit commonly occurs in older individuals without Aβ pathology, in a condition referred to as PART [143]. This indicates that tau pathology in the entorhinal cortex is not specific to AD, and the region is not appropriate for assessment in the early stage. A temporal meta-region of interest (ROI) consisting of the entorhinal, fusiform, and inferior and middle temporal cortices is another candidate and is more specific to AD [4]. However, this ROI may be less sensitive in early stages. In previous studies with cognitively unimpaired individuals with Aβ positivity, only approximately 5% to 10% of the individuals are classified as tau-positive [110, 152]. Interestingly, compared with temporal meta-ROI quantification, visual assessment shows better sensitivity in detecting tau positivity. Even at subthreshold levels of tau PET signal, visual positivity is possible [153]. In addition, although individuals with a visually positive signal might not meet the quantitative threshold for positivity, they tend to show positivity in other AD biomarkers including amyloid PET and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) phosphorylated tau concentration [153].
SUVR is the most common semi-quantitative method to measure radiotracer uptake in an image and is calculated as degree of radiotracer uptake in a target ROI with respect to that in a RR [154,155]. SUVR is a convenient and useful tool for regional comparisons within a subject as well as between subjects; thus, SUVR has been widely used in studies based on brain PET images. As shown in the calculation formula, RR is the key factor that can significantly affect the overall SUVR measurement. Selection of an optimal RR is very important for accurate measurement with low variance [154]. Characteristics of an optimal RR are as follows. First, the region has to be devoid of target molecules that bind with radiotracer or are involved in the pathological process of disease. Second, the region should be free of off-target binding. Last, to minimize spill-in of radioactivity, the region needs to be distant from the region of tested radiotracer measurement.
Cerebellar gray matter satisfies the conditions required for tau PET studies, with absence of tau pathology in neuropathologic studies [53] and low variance in controls [72]. The mid-portion of the cerebellar gray matter such as the inferior cerebellar cortex or cerebellar crus is preferred as an RR since it can minimize spill-in from the occipital lobe and avoid off-target binding in the superior parts of the cerebellar vermis, observed with some other tracers [4,156]. Inferior cerebellar gray matter is a sensitive RR in discriminating group differences cross-sectionally. In a recent study with clinically unimpaired (CU) amyloid-negative individuals, CU amyloid-positive individuals, and MCI amyloid-positive individuals, this RR resulted in robust group differences, along with significant associations with CSF phosphorylated tau [157].
Interestingly, eroded WM may be more sensitive for longitudinal analyses. An eroded subcortical WM or eroded subcortical WM cerebellar composite RR may be more suitable for longitudinal analyses examining regional patterns of change [157-160]. The eroded WM RR more consistently detected significant change over time [157]. However, given that WM has a risk of spill-in due to its close proximity to the cortex, this RR needs to be verified in further studies with individuals with high cortical tau deposition [4].
An optimal processing approach that would minimize the influence of off-target signal is required. However, target or RR selection to reduce off-target signal should be performed carefully to avoid exacerbation of noise in SUVR data. A recent study with 18F-MK6240 reported that tau SUVR data are not obfuscated by noise, although off-target signal introduces noise. It is likely that off-target signal contaminates both reference and target regions, and the influence of off-target signal largely is cancelled out in SUVR data [161].
The partial volume effect (PVE) reduces the quantitative accuracy of an imaging system and is introduced by finite spatial resolution processes of imaging modalities. PET has poor spatial resolution compared with other imaging modalities such as MRI or computed tomography. The PVE is of concern and leads to overestimation or underestimation of radiotracer intensity estimates in PET imaging. Due to PVE, especially in small objects, acquired radioactivity from the object by the PET system differs from the ideal [162]. The PVE is a combination of two distinct phenomena: image blurring and image sampling [162]. Image blurring caused by finite spatial resolution of the imaging system results in spillover between regions and reduction of maximum activity in measured images. Typically, “spill out” of radioactivity into surrounding tissue from a high-activity region leads to underestimation of tracer uptake estimates, while “spill-in” into voxels of interest from a high-activity region leads to overestimation of radiotracer uptake estimates. Image sampling resulted from discrepancy of the actual contours of the radiotracer distribution and the radiotracer distribution is sampled on a voxel grid of PET imaging system. The actual contours of the object containing radiotracer do not match those of the voxels. Therefore, each voxel at the boundary of the target tissue represents the underlying tissues. In other words, the intensity of a particular voxel reflects the tracer concentration not only of the tissue within the voxel, but also that of the surrounding area.
In brain studies with PET, PVE is an important issue because it can influence SUVR measurement. For example, when the size of the target tissue region is small and the RR is adjacent to a high-radioactivity region, SUVR of the target region is likely to be measured as lower than actual. Therefore, partial volume correction (PVC) methods are needed for PVE. In a recent longitudinal cohort study with tau PET data, PVC improved the discriminative accuracy between cognitively impaired and unimpaired individuals cross-sectionally [158]. PVC also reduced the impact of choroid plexus off-target binding on hippocampal signals [148]. The geometric transfer matrix (GTM) method and more novel PVC methods modestly improved the diagnostic accuracy of tau tracer deposit in the hippocampus and the correlations between hippocampal SUVR and cognitive measures [163,164]. In addition, in a recent longitudinal cohort study with tau PET data, among five PVC methods (none, two-compartment, three-compartment, GTM, and tau-specific GTM variant), two-compartment voxel-based PVC showed the most favorable results [158]. However, consensus on the use of PVC has not been reached in tau PET studies. Although an obvious SUVR increase in tracer retention is measured with PVC data, whether PVC has a significant effect on the main results of studies (e.g., diagnostic performance, correlation with cognitive function) [4] and a standard PVC method have not been established. However, despite lack of consensus on the use of PVE in tau PET studies, it is increasingly recommended to report results both with without PVC.
Tau PET imaging enables visualization and quantification of tau pathology, indicating that tau PET imaging has great potential as a useful diagnostic tool for tauopathies. This technology provides great opportunity to elucidate previously unstudied paths of tau pathology in the living human brain and improves understanding of neurodegenerative disorders. For example, temporal and spatial information of tau burden could reveal a relationship with Aβ. These findings may be helpful to address how tau causes cognitive decline in AD, whether via synergistic interactions with Aβ or independently. A growing number of studies has provided valuable results on the usefulness of tau PET, including the ability to detect AD dementia, discriminate stages of AD, distinguish AD from other neurodegenerative diseases, predict the cognitive consequences of AD, and differentiate primary tauopathies from one another. Although the usefulness and diagnostic accuracy of tau PET at an individual level are not established, imaging has shown promise for detection of AD among cognitively unimpaired individuals, for prognostic use in AD, for distinguishing AD dementia from non-AD neurodegenerative disorders, and for differentiating non-AD tauopathies such as CBD and PSP from controls at a group level. However, there are several challenges that limit the utility of tau PET. First, off-target binding is a major drawback that weakens the possibility of tau PET as a diagnostic tool. Tracers can present large binding overlap with known off-target binding regions, which impedes reliable detection and quantification of tau burden especially in non-AD tauopathies. Selection of the optimal RR and application of PVC methods are also important methodological issues that could affect the potential use of tau PET imaging. Over the past decade, there have been continued developments for better tau tracers with improved sensitivity and specificity for tau pathology without off-target binding. These first- and second-generation tracers are now under investigation. More data are required to fully evaluate the potential of these tracers as imaging biomarkers in accurately characterizing tau burden. Additionally, it will be necessary to discuss further directions in the field of tau PET research. Head-to-head comparison with other biomarkers such as CSF and plasma biomarkers (e.g., p-tau and the Aβ42/40 ratio) is an important step to correctly interpret the results of different biomarkers and is required to develop an appropriate guide for use. Recent studies have shown that tau PET tracer binding correlates strongly with CSF tau biomarkers [165,166]. Establishing a standard method of tau PET measurement has great value for patient selection and treatment monitoring in clinical trials. Long-term study design with a more diverse population of patients could be helpful to further our understanding of the role of tau PET.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Sang Won Seo has been editorial board of Precision and Future Medicine since December 2017. He was not involved in the review process of this review aricle.
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: HL, YG, SWS, SHM.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: HL, YG.
Drafting the work or revising: HL, SHM
Final approval of the manuscript: HL, YG, SWS, SHM.
Fig. 1.
Increase of tau positron emission tomography (PET) publications. Records were obtained from a database (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) using search queries that referred to the recent review paper [4].

Fig. 2.
Off-target binding of first-generation tau positron emission tomography (PET) tracers. (A) 18F-AV1451 PET images in health volunteer showing off-target binding in basal ganglia, choroid plexus, retinal, and pituitary. (B) 18F-THK5351 PET images showing high signal intensity in basal ganglia, which is explained by binding to monoamine oxidase B.

Fig. 4.
Patterns of uptake observed with 18F-AV-1451 at different disease stages. Axial positron emission tomography (PET) images of 18F- AV1451 from one cognitively normal with Korean-Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) of 28 (A), two mild cognitive impairment with K-MMSE of 22, 21 (B, C, respectively), and one Alzheimer dementia with K-MMSE of five (D) patients. Signal intensity and extent increase with disease severity, which are successively involving temporal, parietal, frontal, and occipital cortices.
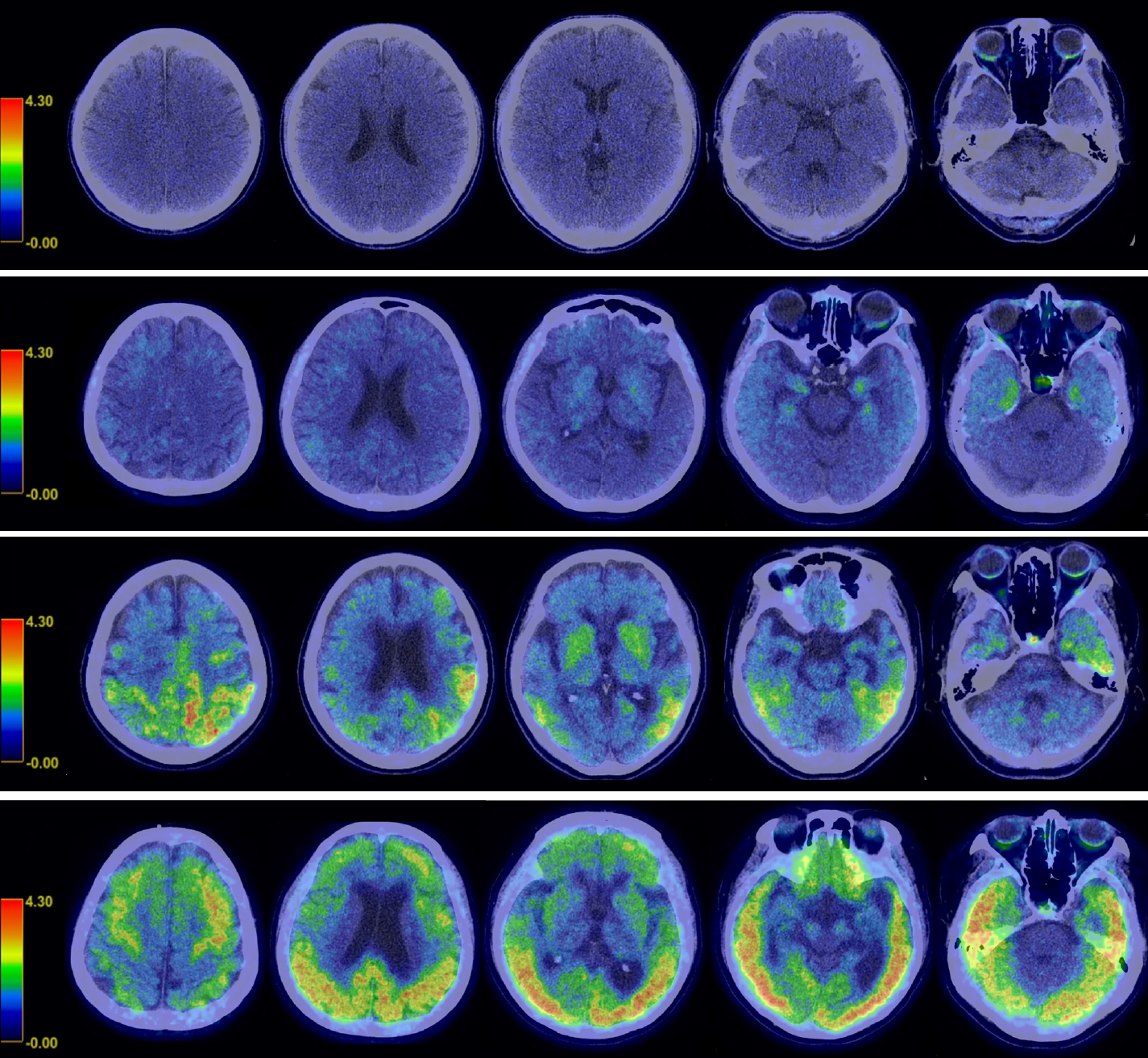
Table 1.
Binding characteristics of representative first- and second-generation tau tracers
| Generation | Tracer | Affinity | On-target | Off-target | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | 18F-AV1451 (18F-T807, 18F-flortaucipir, and TauvidTM) | Kd=14.6 nM (AD brain sections) | PHFs, pretangles, mature tangles, neuritic and primitive plaques | MAO-A (low affinity) | [18,23,33,46,47,77,97-100] |
| Kd=1.4–3.72 nM (enthorhinal cortex) | MAO-B (mixed result) | ||||
| Kd=0.63–1.70 nM (frontal cortex) | Basal ganglia, choroid plexus, midbrain, melanin-containing cells | ||||
| 18F-THK5351 | Kd=2.9 nM | NFTs, thread like structures in white matter, tufted astrocytes | MAO-B | [18,23,43,101,102] | |
| Basal ganglia, thalamus, midbrain, and periaqueductal gray matter | |||||
| 11C-PBB3 | Kd=2.5 nM (NFT-rich AD brain tissue) | NFTs, neuropil threads, neuritic plaques; pick bodies, tau inclusion in PiD, PSP, CBD | No off-target binding to MAO-A, MAO-B | [18,23,45,82,103] | |
| Dural venous sinuses, basal ganglia, thalamus | |||||
| Second | 18F-MK6240 | Kd=~0.3 nM (NFT-rich AD brain homogenates) | NFTs | No off-target binding to MAO-A, MAO-B | [18,23,95,100,104] |
| Red nucleus, meninges | |||||
| 18F-RO948 (18F-RO6958948) | IC50=18.5 | NFTs, neuropil threads | No off-target binding to MAO-A, MAO-B | [18,23,89,105] | |
| 18F-PI2620 | IC50=1.8 nM (AD brain tissue) | 3R tau from Pick, 4R from PSP | No off-target binding to MAO-A, MAO-B | [18,23,90] | |
| 18F-GTP1 | 14.9±0.43 nM (tau-positive brain tissue) | NFTs | No off-target binding to MAO-A, MAO-B | [18,23,91] | |
| 18F-JNJ-64326067 (18F-JNJ-067) | Kd=2.4 nM | NFTs | No off-target binding to MAO-A, MAO-B | [18,23,106] |
REFERENCES
1. Noble W, Hanger DP, Miller CC, Lovestone S. The importance of tau phosphorylation for neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurol 2013;4:83.



2. Niblock M, Gallo JM. Tau alternative splicing in familial and sporadic tauopathies. Biochem Soc Trans 2012;40:677–80.



3. Saint-Aubert L, Lemoine L, Chiotis K, Leuzy A, Rodriguez-Vieitez E, Nordberg A. Tau PET imaging: present and future directions. Mol Neurodegener 2017;12:19.




4. Groot C, Villeneuve S, Smith R, Hansson O, Ossenkoppele R. Tau PET imaging in neurodegenerative disorders. J Nucl Med 2022;63(Suppl 1):20S–6S.


5. Hanger DP, Anderton BH, Noble W. Tau phosphorylation: the therapeutic challenge for neurodegenerative disease. Trends Mol Med 2009;15:112–9.


6. Orr ME, Sullivan AC, Frost B. A brief overview of tauopathy: causes, consequences, and therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2017;38:637–48.



7. Buee L, Bussiere T, Buee-Scherrer V, Delacourte A, Hof PR. Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 2000;33:95–130.

8. Irwin DJ. Tauopathies as clinicopathological entities. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2016;22 Suppl 1:S29–33.


9. Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ. Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci 2001;24:1121–59.


10. Sergeant N, Delacourte A, Buee L. Tau protein as a differential biomarker of tauopathies. Biochim Biophys Acta 2005;1739:179–97.


11. Williams DR. Tauopathies: classification and clinical update on neurodegenerative diseases associated with microtubule-associated protein tau. Intern Med J 2006;36:652–60.


12. Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 1991;82:239–59.



13. Forman MS, Zhukareva V, Bergeron C, Chin SS, Grossman M, Clark C, et al. Signature tau neuropathology in gray and white matter of corticobasal degeneration. Am J Pathol 2002;160:2045–53.



14. Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J. Progressive supranuclear palsy: a heterogeneous degeneration involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch Neurol 1964;10:333–59.


15. Chen S, Townsend K, Goldberg TE, Davies P, Conejero-Goldberg C. MAPT isoforms: differential transcriptional profiles related to 3R and 4R splice variants. J Alzheimers Dis 2010;22:1313–29.



17. Chien DT, Bahri S, Szardenings AK, Walsh JC, Mu F, Su MY, et al. Early clinical PET imaging results with the novel PHF-tau radioligand [F-18]-T807. J Alzheimers Dis 2013;34:457–68.


18. Leuzy A, Chiotis K, Lemoine L, Gillberg PG, Almkvist O, Rodriguez-Vieitez E, et al. Tau PET imaging in neurodegenerative tauopathies-still a challenge. Mol Psychiatry 2019;24:1112–34.




19. Shah M, Catafau AM. Molecular imaging insights into neurodegeneration: focus on tau PET radiotracers. J Nucl Med 2014;55:871–4.


20. Halldin C, Gulyas B, Farde L. PET studies with carbon-11 radioligands in neuropsychopharmacological drug development. Curr Pharm Des 2001;7:1907–29.


21. Laruelle M, Slifstein M, Huang Y. Relationships between radiotracer properties and image quality in molecular imaging of the brain with positron emission tomography. Mol Imaging Biol 2003;5:363–75.


22. Pike VW. PET radiotracers: crossing the blood-brain barrier and surviving metabolism. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2009;30:431–40.



23. Lois C, Gonzalez I, Johnson KA, Price JC. PET imaging of tau protein targets: a methodology perspective. Brain Imaging Behav 2019;13:333–44.




24. Dani M, Brooks DJ, Edison P. Tau imaging in neurodegenerative diseases. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2016;43:1139–50.




25. Villemagne VL, Furumoto S, Fodero-Tavoletti MT, Mulligan RS, Hodges J, Harada R, et al. In vivo evaluation of a novel tau imaging tracer for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2014;41:816–26.



26. Harada R, Okamura N, Furumoto S, Tago T, Yanai K, Arai H, et al. Characteristics of tau and its ligands in PET imaging. Biomolecules 2016;6:7.



27. Shoghi-Jadid K, Small GW, Agdeppa ED, Kepe V, Ercoli LM, Siddarth P, et al. Localization of neurofibrillary tangles and beta-amyloid plaques in the brains of living patients with Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2002;10:24–35.


28. Agdeppa ED, Kepe V, Liu J, Flores-Torres S, Satyamurthy N, Petric A, et al. Binding characteristics of radiofluorinated 6-dialkylamino-2-naphthylethylidene derivatives as positron emission tomography imaging probes for beta-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 2001;21:RC189.



29. Thompson PW, Ye L, Morgenstern JL, Sue L, Beach TG, Judd DJ, et al. Interaction of the amyloid imaging tracer FDDNP with hallmark Alzheimer’s disease pathologies. J Neurochem 2009;109:623–30.



30. Wolters EE, Dodich A, Boccardi M, Corre J, Drzezga A, Hansson O, et al. Clinical validity of increased cortical uptake of [18F]flortaucipir on PET as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease in the context of a structured 5-phase biomarker development framework. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2021;48:2097–109.




31. Chiotis K, Dodich A, Boccardi M, Festari C, Drzezga A, Hansson O, et al. Clinical validity of increased cortical binding of tau ligands of the THK family and PBB3 on PET as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in the context of a structured 5-phase development framework. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2021;48:2086–96.




32. Holt DP, Ravert HT, Dannals RF. Synthesis and quality control of [(18)F]T807 for tau PET imaging. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 2016;59:411–5.


33. Xia CF, Arteaga J, Chen G, Gangadharmath U, Gomez LF, Kasi D, et al. [(18)F]T807, a novel tau positron emission tomography imaging agent for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 2013;9:666–76.



34. Fodero-Tavoletti MT, Okamura N, Furumoto S, Mulligan RS, Connor AR, McLean CA, et al. 18F-THK523: a novel in vivo tau imaging ligand for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2011;134(Pt 4):1089–100.


35. Tago T, Furumoto S, Okamura N, Harada R, Adachi H, Ishikawa Y, et al. Structure-activity relationship of 2-arylquinolines as PET imaging tracers for tau pathology in Alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med 2016;57:608–14.


36. Okamura N, Furumoto S, Harada R, Tago T, Yoshikawa T, Fodero-Tavoletti M, et al. Novel 18F-labeled arylquinoline derivatives for noninvasive imaging of tau pathology in Alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med 2013;54:1420–7.


37. Stepanov V, Svedberg M, Jia Z, Krasikova R, Lemoine L, Okamura N, et al. Development of [11C]/[3H]THK-5351: a potential novel carbon-11 tau imaging PET radioligand. Nucl Med Biol 2017;46:50–3.


38. Wang M, Gao M, Xu Z, Zheng QH. Synthesis of a PET tau tracer [(11)C]PBB3 for imaging of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015;25:4587–92.


39. Hashimoto H, Kawamura K, Igarashi N, Takei M, Fujishiro T, Aihara Y, et al. Radiosynthesis, photoisomerization, biodistribution, and metabolite analysis of 11C-PBB3 as a clinically useful PET probe for imaging of tau pathology. J Nucl Med 2014;55:1532–8.


40. Yousefzadeh-Nowshahr E, Winter G, Bohn P, Kneer K, von Arnim CA, Otto M, et al. Quantitative analysis of regional distribution of tau pathology with 11C-PBB3-PET in a clinical setting. PLoS One 2022;17:e0266906.



41. Chien DT, Szardenings AK, Bahri S, Walsh JC, Mu F, Xia C, et al. Early clinical PET imaging results with the novel PHF-tau radioligand [F18]-T808. J Alzheimers Dis 2014;38:171–84.


42. Jie CV, Treyer V, Schibli R, Mu L. Tauvid(TM): the first FDA-approved PET tracer for imaging tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2021;14:110.


43. Betthauser TJ, Lao PJ, Murali D, Barnhart TE, Furumoto S, Okamura N, et al. In vivo comparison of tau radioligands 18F-THK-5351 and 18F-THK-5317. J Nucl Med 2017;58:996–1002.



44. Harada R, Okamura N, Furumoto S, Furukawa K, Ishiki A, Tomita N, et al. 18F-THK5351: a novel PET radiotracer for imaging neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med 2016;57:208–14.


45. Kimura Y, Ichise M, Ito H, Shimada H, Ikoma Y, Seki C, et al. PET quantification of tau pathology in human brain with 11C-PBB3. J Nucl Med 2015;56:1359–65.


46. Lowe VJ, Curran G, Fang P, Liesinger AM, Josephs KA, Parisi JE, et al. An autoradiographic evaluation of AV-1451 tau PET in dementia. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2016;4:58.




47. Marquie M, Normandin MD, Vanderburg CR, Costantino IM, Bien EA, Rycyna LG, et al. Validating novel tau positron emission tomography tracer [F-18]-AV-1451 (T807) on postmortem brain tissue. Ann Neurol 2015;78:787–800.



48. Sander K, Lashley T, Gami P, Gendron T, Lythgoe MF, Rohrer JD, et al. Characterization of tau positron emission tomography tracer [18F]AV-1451 binding to postmortem tissue in Alzheimer’s disease, primary tauopathies, and other dementias. Alzheimers Dement 2016;12:1116–24.



49. Fleisher AS, Pontecorvo MJ, Devous MD Sr, Lu M, Arora AK, Truocchio SP, et al. Positron emission tomography imaging with [18F]flortaucipir and postmortem assessment of Alzheimer disease neuropathologic changes. JAMA Neurol 2020;77:829–39.



50. Soleimani-Meigooni DN, Iaccarino L, La Joie R, Baker S, Bourakova V, Boxer AL, et al. 18F-flortaucipir PET to autopsy comparisons in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain 2020;143:3477–94.




51. Lowe VJ, Lundt ES, Albertson SM, Min HK, Fang P, Przybelski SA, et al. Tau-positron emission tomography correlates with neuropathology findings. Alzheimers Dement 2020;16:561–71.




52. Pontecorvo MJ, Keene CD, Beach TG, Montine TJ, Arora AK, Devous MD Sr, et al. Comparison of regional flortaucipir PET with quantitative tau immunohistochemistry in three subjects with Alzheimer’s disease pathology: a clinicopathological study. EJNMMI Res 2020;10:65.




53. Smith R, Wibom M, Pawlik D, Englund E, Hansson O. Correlation of in vivo [18F]flortaucipir with postmortem Alzheimer disease tau pathology. JAMA Neurol 2019;76:310–7.



54. Smith R, Puschmann A, Scholl M, Ohlsson T, van Swieten J, Honer M, et al. 18F-AV-1451 tau PET imaging correlates strongly with tau neuropathology in MAPT mutation carriers. Brain 2016;139(Pt 9):2372–9.



55. Tsai RM, Bejanin A, Lesman-Segev O, LaJoie R, Visani A, Bourakova V, et al. 18F-flortaucipir (AV-1451) tau PET in frontotemporal dementia syndromes. Alzheimers Res Ther 2019;11:13.




56. Cho H, Baek MS, Choi JY, Lee SH, Kim JS, Ryu YH, et al. 18F-AV-1451 binds to motor-related subcortical gray and white matter in corticobasal syndrome. Neurology 2017;89:1170–8.


57. Smith R, Scholl M, Widner H, van Westen D, Svenningsson P, Hagerstrom D, et al. In vivo retention of 18F-AV-1451 in corticobasal syndrome. Neurology 2017;89:845–53.



58. Cho H, Choi JY, Hwang MS, Lee SH, Ryu YH, Lee MS, et al. Subcortical 18F-AV-1451 binding patterns in progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord 2017;32:134–40.



59. Smith R, Schain M, Nilsson C, Strandberg O, Olsson T, Hagerstrom D, et al. Increased basal ganglia binding of 18F-AV-1451 in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord 2017;32:108–14.




60. Whitwell JL, Lowe VJ, Tosakulwong N, Weigand SD, Senjem ML, Schwarz CG, et al. [18F]AV-1451 tau positron emission tomography in progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord 2017;32:124–33.




61. Smith R, Scholl M, Honer M, Nilsson CF, Englund E, Hansson O. Tau neuropathology correlates with FDG-PET, but not AV-1451-PET, in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 2017;133:149–51.




62. Josephs KA, Whitwell JL, Tacik P, Duffy JR, Senjem ML, Tosakulwong N, et al. [18F]AV-1451 tau-PET uptake does correlate with quantitatively measured 4R-tau burden in autopsy-confirmed corticobasal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 2016;132:931–3.




63. McMillan CT, Irwin DJ, Nasrallah I, Phillips JS, Spindler M, Rascovsky K, et al. Multimodal evaluation demonstrates in vivo 18F-AV-1451 uptake in autopsy-confirmed corticobasal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 2016;132:935–7.




64. Smith R, Pawlik D, Nilsson CF, Englund E, Hansson O. [18F]Flortaucipir distinguishes Alzheimer’s disease from progressive supranuclear palsy pathology in a mixed-pathology case. Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:411–3.




65. Baker SL, Lockhart SN, Price JC, He M, Huesman RH, Schonhaut D, et al. Reference tissue-based kinetic evaluation of 18F-AV-1451 for tau imaging. J Nucl Med 2017;58:332–8.



66. Shcherbinin S, Schwarz AJ, Joshi A, Navitsky M, Flitter M, Shankle WR, et al. Kinetics of the tau PET tracer 18F-AV-1451 (T807) in subjects with normal cognitive function, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med 2016;57:1535–42.


67. Wooten DW, Guehl NJ, Verwer EE, Shoup TM, Yokell DL, Zubcevik N, et al. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of the tau PET radiotracer 18F-T807 (18F-AV-1451) in human subjects. J Nucl Med 2017;58:484–91.



68. Jonasson M, Wall A, Chiotis K, Saint-Aubert L, Wilking H, Sprycha M, et al. Tracer kinetic analysis of (S)-¹8F-THK5117 as a PET tracer for assessing tau pathology. J Nucl Med 2016;57:574–81.


69. Lockhart SN, Baker SL, Okamura N, Furukawa K, Ishiki A, Furumoto S, et al. Dynamic PET measures of tau accumulation in cognitively normal older adults and Alzheimer’s disease patients measured using [18F] THK-5351. PLoS One 2016;11:e0158460.



70. Hahn A, Schain M, Erlandsson M, Sjolin P, James GM, Strandberg OT, et al. Modeling strategies for quantification of in vivo 18F-AV-1451 binding in patients with tau pathology. J Nucl Med 2017;58:623–31.


71. Barret O, Alagille D, Sanabria S, Comley RA, Weimer RM, Borroni E, et al. Kinetic modeling of the tau PET tracer 18F-AV-1451 in human healthy volunteers and Alzheimer disease subjects. J Nucl Med 2017;58:1124–31.


72. Baker SL, Harrison TM, Maass A, La Joie R, Jagust WJ. Effect of off-target binding on 18F-flortaucipir variability in healthy controls across the life span. J Nucl Med 2019;60:1444–51.



73. Harada R, Ishiki A, Kai H, Sato N, Furukawa K, Furumoto S, et al. Correlations of 18F-THK5351 PET with postmortem burden of tau and astrogliosis in Alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med 2018;59:671–4.


74. Kim HJ, Cho H, Park S, Jang H, Ryu YH, Choi JY, et al. THK5351 and flortaucipir PET with pathological correlation in a Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease patient: a case report. BMC Neurol 2019;19:211.




75. Smith R, Scholl M, Leuzy A, Jogi J, Ohlsson T, Strandberg O, et al. Head-to-head comparison of tau positron emission tomography tracers [18F]flortaucipir and [18F]RO948. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2020;47:342–54.



76. Gogola A, Minhas DS, Villemagne VL, Cohen AD, Mountz JM, Pascoal TA, et al. Direct comparison of the tau PET tracers 18F-Flortaucipir and 18F-MK-6240 in human subjects. J Nucl Med 2022;63:108–16.



77. Vermeiren C, Motte P, Viot D, Mairet-Coello G, Courade JP, Citron M, et al. The tau positron-emission tomography tracer AV-1451 binds with similar affinities to tau fibrils and monoamine oxidases. Mov Disord 2018;33:273–81.



78. Hansen AK, Brooks DJ, Borghammer P. MAO-B inhibitors do not block in vivo flortaucipir([18F]-AV-1451) binding. Mol Imaging Biol 2018;20:356–60.



79. Jang YK, Lyoo CH, Park S, Oh SJ, Cho H, Oh M, et al. Head to head comparison of [18F] AV-1451 and [18F] THK5351 for tau imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2018;45:432–42.



80. Smith R, Santillo AF, Waldo ML, Strandberg O, Berron D, Vestberg S, et al. 18F-Flortaucipir in TDP-43 associated frontotemporal dementia. Sci Rep 2019;9:6082.




81. Mann DM, Snowden JS. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: pathogenesis, pathology and pathways to phenotype. Brain Pathol 2017;27:723–36.




82. Maruyama M, Shimada H, Suhara T, Shinotoh H, Ji B, Maeda J, et al. Imaging of tau pathology in a tauopathy mouse model and in Alzheimer patients compared to normal controls. Neuron 2013;79:1094–108.


83. Mattsson N, Scholl M, Strandberg O, Smith R, Palmqvist S, Insel PS, et al. 18F-AV-1451 and CSF T-tau and P-tau as biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 2017;9:1212–23.




84. Gobbi LC, Knust H, Korner M, Honer M, Czech C, Belli S, et al. Identification of three novel radiotracers for imaging aggregated tau in Alzheimer’s disease with positron emission tomography. J Med Chem 2017;60:7350–70.


85. Declercq L, Rombouts F, Koole M, Fierens K, Marien J, Langlois X, et al. Preclinical evaluation of 18F-JNJ64349311, a novel PET tracer for tau imaging. J Nucl Med 2017;58:975–81.


86. Aguero C, Dhaynaut M, Normandin MD, Amaral AC, Guehl NJ, Neelamegam R, et al. Autoradiography validation of novel tau PET tracer [F-18]-MK-6240 on human postmortem brain tissue. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2019;7:37.




87. Bischof GN, Dodich A, Boccardi M, van Eimeren T, Festari C, Barthel H, et al. Clinical validity of second-generation tau PET tracers as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in the context of a structured 5-phase development framework. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2021;48:2110–20.




88. Koole M, Lohith TG, Valentine JL, Bennacef I, Declercq R, Reynders T, et al. Preclinical safety evaluation and human dosimetry of [18F]MK-6240, a novel PET tracer for imaging neurofibrillary tangles. Mol Imaging Biol 2020;22:173–80.



89. Wong DF, Comley RA, Kuwabara H, Rosenberg PB, Resnick SM, Ostrowitzki S, et al. Characterization of 3 novel tau radiopharmaceuticals, 11C-RO-963, 11C-RO-643, and 18F-RO-948, in healthy controls and in Alzheimer subjects. J Nucl Med 2018;59:1869–76.



90. Mueller A, Bullich S, Barret O, Madonia J, Berndt M, Papin C, et al. Tau PET imaging with 18F-PI-2620 in patients with Alzheimer disease and healthy controls: a first-in-humans study. J Nucl Med 2020;61:911–9.



91. Sanabria Bohorquez S, Marik J, Ogasawara A, Tinianow JN, Gill HS, Barret O, et al. [18F]GTP1 (genentech tau probe 1), a radioligand for detecting neurofibrillary tangle tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2019;46:2077–89.



92. Brendel M, Barthel H, van Eimeren T, Marek K, Beyer L, Song M, et al. Assessment of 18F-PI-2620 as a biomarker in progressive supranuclear palsy. JAMA Neurol 2020;77:1408–19.


93. Tagai K, Ono M, Kubota M, Kitamura S, Takahata K, Seki C, et al. High-contrast in vivo imaging of tau pathologies in Alzheimer’s and non-Alzheimer’s disease tauopathies. Neuron 2021;109:42–58.


94. Tezuka T, Takahata K, Seki M, Tabuchi H, Momota Y, Shiraiwa M, et al. Evaluation of [18F]PI-2620, a second-generation selective tau tracer, for assessing four-repeat tauopathies. Brain Commun 2021;3:fcab190.




95. Betthauser TJ, Cody KA, Zammit MD, Murali D, Converse AK, Barnhart TE, et al. In vivo characterization and quantification of neurofibrillary tau PET radioligand 18F-MK-6240 in humans from Alzheimer disease dementia to young controls. J Nucl Med 2019;60:93–9.



96. Smith R, Strandberg O, Leuzy A, Betthauser TJ, Johnson SC, Pereira JB, et al. Sex differences in off-target binding using tau positron emission tomography. Neuroimage Clin 2021;31:102708.



97. Hansen AK, Knudsen K, Lillethorup TP, Landau AM, Parbo P, Fedorova T, et al. In vivo imaging of neuromelanin in Parkinson’s disease using 18F-AV-1451 PET. Brain 2016;139(Pt 7):2039–49.


98. Marquie M, Normandin MD, Meltzer AC, Siao Tick Chong M, Andrea NV, Anton-Fernandez A, et al. Pathological correlations of [F-18]-AV-1451 imaging in non-Alzheimer tauopathies. Ann Neurol 2017;81:117–28.




99. Ikonomovic MD, Abrahamson EE, Price JC, Mathis CA, Klunk WE. [F-18]AV-1451 positron emission tomography retention in choroid plexus: more than “off-target” binding. Ann Neurol 2016;80:307–8.



100. Hostetler ED, Walji AM, Zeng Z, Miller P, Bennacef I, Salinas C, et al. Preclinical characterization of 18F-MK-6240, a promising PET tracer for in vivo quantification of human neurofibrillary tangles. J Nucl Med 2016;57:1599–606.


101. Harada R, Furumoto S, Tago T, Furukawa K, Ishiki A, Tomita N, et al. Characterization of the radiolabeled metabolite of tau PET tracer 18F-THK5351. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2016;43:2211–8.



102. Harada R, Okamura N, Furumoto S, Furukawa K, Ishiki A, Tomita N, et al. [(18)F]THK-5117 PET for assessing neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2015;42:1052–61.



103. Ono M, Sahara N, Kumata K, Ji B, Ni R, Koga S, et al. Distinct binding of PET ligands PBB3 and AV-1451 to tau fibril strains in neurodegenerative tauopathies. Brain 2017;140:764–80.



104. Walji AM, Hostetler ED, Selnick H, Zeng Z, Miller P, Bennacef I, et al. Discovery of 6-(Fluoro-(18)F)-3-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)isoquinolin-5-amine ([(18)F]-MK-6240): a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agent for quantification of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). J Med Chem 2016;59:4778–89.

105. Honer M, Gobbi L, Knust H, Kuwabara H, Muri D, Koerner M, et al. Preclinical evaluation of 18F-RO6958948, 11C-RO6931643, and 11C-RO6924963 as novel PET radiotracers for imaging tau aggregates in Alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med 2018;59:675–81.



106. Baker SL, Provost K, Thomas W, Whitman AJ, Janabi M, Schmidt ME, et al. Evaluation of [18F]-JNJ-64326067-AAA tau PET tracer in humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2021;41:3302–13.




107. Sexton C, Snyder H, Beher D, Boxer AL, Brannelly P, Brion JP, et al. Current directions in tau research: highlights from Tau 2020. Alzheimers Dement 2022;18:988–1007.



108. Zhang Y, Wu KM, Yang L, Dong Q, Yu JT. Tauopathies: new perspectives and challenges. Mol Neurodegener 2022;17:28.




110. Ossenkoppele R, Rabinovici GD, Smith R, Cho H, Scholl M, Strandberg O, et al. Discriminative accuracy of [18F]flortaucipir positron emission tomography for Alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA 2018;320:1151–62.



111. Jack CR, Wiste HJ, Botha H, Weigand SD, Therneau TM, Knopman DS, et al. The bivariate distribution of amyloid-β and tau: relationship with established neurocognitive clinical syndromes. Brain 2019;142:3230–42.




112. Leuzy A, Pascoal TA, Strandberg O, Insel P, Smith R, Mattsson-Carlgren N, et al. A multicenter comparison of [18F]flortaucipir, [18F]RO948, and [18F]MK6240 tau PET tracers to detect a common target ROI for differential diagnosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2021;48:2295–305.




113. Altomare D, Caprioglio C, Assal F, Allali G, Mendes A, Ribaldi F, et al. Diagnostic value of amyloid-PET and tau-PET: a head-to-head comparison. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2021;48:2200–11.




114. Ossenkoppele R, Schonhaut DR, Scholl M, Lockhart SN, Ayakta N, Baker SL, et al. Tau PET patterns mirror clinical and neuroanatomical variability in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2016;139(Pt 5):1551–67.



115. Dronse J, Fliessbach K, Bischof GN, von Reutern B, Faber J, Hammes J, et al. In vivo patterns of tau pathology, amyloid-β burden, and neuronal dysfunction in clinical variants of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2017;55:465–71.


116. Ossenkoppele R, Schonhaut DR, Baker SL, O’Neil JP, Janabi M, Ghosh PM, et al. Tau, amyloid, and hypometabolism in a patient with posterior cortical atrophy. Ann Neurol 2015;77:338–42.


117. Vogel JW, Young AL, Oxtoby NP, Smith R, Ossenkoppele R, Strandberg OT, et al. Four distinct trajectories of tau deposition identified in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 2021;27:871–81.




118. Bateman RJ, Aisen PS, De Strooper B, Fox NC, Lemere CA, Ringman JM, et al. Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease: a review and proposal for the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 2011;3:1.



119. Gordon BA, Blazey TM, Christensen J, Dincer A, Flores S, Keefe S, et al. Tau PET in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease: relationship with cognition, dementia and other biomarkers. Brain 2019;142:1063–76.


120. Krishnadas N, Huang K, Schultz SA, Dore V, Bourgeat P, Goh AM, et al. Visually identified tau 18F-MK6240 PET patterns in symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2022;88:1627–37.



121. Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Hampel H, Molinuevo JL, Blennow K, et al. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: the IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol 2014;13:614–29.


122. Dubois B, Hampel H, Feldman HH, Scheltens P, Aisen P, Andrieu S, et al. Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: definition, natural history, and diagnostic criteria. Alzheimers Dement 2016;12:292–323.




123. Leuzy A, Smith R, Ossenkoppele R, Santillo A, Borroni E, Klein G, et al. Diagnostic performance of RO948 F 18 tau positron emission tomography in the differentiation of Alzheimer disease from other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA Neurol 2020;77:955–65.


124. Pascoal TA, Therriault J, Benedet AL, Savard M, Lussier FZ, Chamoun M, et al. 18F-MK-6240 PET for early and late detection of neurofibrillary tangles. Brain 2020;143:2818–30.



125. Small SA, Duff K. Linking Abeta and tau in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: a dual pathway hypothesis. Neuron 2008;60:534–42.



126. Jack CR Jr, Bennett DA, Blennow K, Carrillo MC, Dunn B, Haeberlein SB, et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 2018;14:535–62.




127. Ossenkoppele R, Smith R, Mattsson-Carlgren N, Groot C, Leuzy A, Strandberg O, et al. Accuracy of tau positron emission tomography as a prognostic marker in preclinical and prodromal Alzheimer disease: a head-to-head comparison against amyloid positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. JAMA Neurol 2021;78:961–71.



128. Pichet Binette A, Vachon-Presseau E, Morris J, Bateman R, Benzinger T, Collins DL, et al. Amyloid and tau pathology associations with personality traits, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and cognitive lifestyle in the preclinical phases of sporadic and autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Psychiatry 2021;89:776–85.

129. Cho H, Choi JY, Lee HS, Lee JH, Ryu YH, Lee MS, et al. Progressive tau accumulation in Alzheimer disease: 2-year follow-up study. J Nucl Med 2019;60:1611–21.



130. Pontecorvo MJ, Devous MD, Kennedy I, Navitsky M, Lu M, Galante N, et al. A multicentre longitudinal study of flortaucipir (18F) in normal ageing, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Brain 2019;142:1723–35.




131. Lu M, Pontecorvo MJ, Devous MD Sr, Arora AK, Galante N, McGeehan A, et al. Aggregated tau measured by visual interpretation of flortaucipir positron emission tomography and the associated risk of clinical progression of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease: results from 2 phase III clinical trials. JAMA Neurol 2021;78:445–53.


132. La Joie R, Visani AV, Baker SL, Brown JA, Bourakova V, Cha J, et al. Prospective longitudinal atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease correlates with the intensity and topography of baseline tau-PET. Sci Transl Med 2020;12:eaau5732.



133. Chiotis K, Saint-Aubert L, Savitcheva I, Jelic V, Andersen P, Jonasson M, et al. Imaging in-vivo tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease with THK5317 PET in a multimodal paradigm. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2016;43:1686–99.




134. Ishiki A, Harada R, Okamura N, Tomita N, Rowe CC, Villemagne VL, et al. Tau imaging with [18F]THK-5351 in progressive supranuclear palsy. Eur J Neurol 2017;24:130–6.



135. Kikuchi A, Okamura N, Hasegawa T, Harada R, Watanuki S, Funaki Y, et al. In vivo visualization of tau deposits in corticobasal syndrome by 18F-THK5351 PET. Neurology 2016;87:2309–16.



136. Mattsson N, Smith R, Strandberg O, Palmqvist S, Scholl M, Insel PS, et al. Comparing 18F-AV-1451 with CSF t-tau and p-tau for diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2018;90:e388. –95.



137. Palmqvist S, Janelidze S, Quiroz YT, Zetterberg H, Lopera F, Stomrud E, et al. Discriminative accuracy of plasma phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA 2020;324:772–81.


138. Horvath J, Herrmann FR, Burkhard PR, Bouras C, Kovari E. Neuropathology of dementia in a large cohort of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2013;19:864–8.


139. Jellinger KA, Attems J. Prevalence and impact of vascular and Alzheimer pathologies in Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 2008;115:427–36.



140. Jellinger KA, Seppi K, Wenning GK, Poewe W. Impact of coexistent Alzheimer pathology on the natural history of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2002;109:329–39.



141. Gomperts SN, Marquie M, Locascio JJ, Bayer S, Johnson KA, Growdon JH. PET radioligands reveal the basis of dementia in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurodegener Dis 2016;16:118–24.



142. Kantarci K, Lowe VJ, Boeve BF, Senjem ML, Tosakulwong N, Lesnick TG, et al. AV-1451 tau and β-amyloid positron emission tomography imaging in dementia with Lewy bodies. Ann Neurol 2017;81:58–67.



143. Crary JF, Trojanowski JQ, Schneider JA, Abisambra JF, Abner EL, Alafuzoff I, et al. Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): a common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathol 2014;128:755–66.




144. Duyckaerts C, Braak H, Brion JP, Buee L, Del Tredici K, Goedert M, et al. PART is part of Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol 2015;129:749–56.




145. Cho H, Choi JY, Hwang MS, Lee JH, Kim YJ, Lee HM, et al. Tau PET in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2016;87:375–83.


146. Sepulcre J, Schultz AP, Sabuncu M, Gomez-Isla T, Chhatwal J, Becker A, et al. In vivo tau, amyloid, and gray matter profiles in the aging brain. J Neurosci 2016;36:7364–74.



147. Schwarz AJ, Yu P, Miller BB, Shcherbinin S, Dickson J, Navitsky M, et al. Regional profiles of the candidate tau PET ligand 18F-AV-1451 recapitulate key features of Braak histopathological stages. Brain 2016;139(Pt 5):1539–50.


148. Mormino EC, Papp KV, Rentz DM, Schultz AP, LaPoint M, Amariglio R, et al. Heterogeneity in suspected non-Alzheimer disease pathophysiology among clinically normal older individuals. JAMA Neurol 2016;73:1185–91.



149. Villemagne VL, Lopresti BJ, Dore V, Tudorascu D, Ikonomovic MD, Burnham S, et al. What is T+?: a Gordian knot of tracers, thresholds, and topographies. J Nucl Med 2021;62:614–9.


150. Maass A, Landau S, Baker SL, Horng A, Lockhart SN, La Joie R, et al. Comparison of multiple tau-PET measures as biomarkers in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2017;157:448–63.


151. Seibyl JP, DuBois JM, Racine A, Collins J, Guo Q, Wooten D, et al. A visual interpretation algorithm for assessing brain tauopathy with 18F-MK-6240 PET. J Nucl Med 2023;64:444–51.



152. Ossenkoppele R, Jansen WJ, Rabinovici GD, Knol DL, van der Flier WM, van Berckel BN, et al. Prevalence of amyloid PET positivity in dementia syndromes: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2015;313:1939–49.



153. Provost K, Iaccarino L, Soleimani-Meigooni DN, Baker S, Edwards L, Eichenlaub U, et al. Comparing ATN-T designation by tau PET visual reads, tau PET quantification, and CSF PTau181 across three cohorts. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2021;48:2259–71.




154. Vemuri P, Lowe VJ, Knopman DS, Senjem ML, Kemp BJ, Schwarz CG, et al. Tau-PET uptake: regional variation in average SUVR and impact of amyloid deposition. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 2016;6:21–30.




155. Bullich S, Villemagne VL, Catafau AM, Jovalekic A, Koglin N, Rowe CC, et al. Optimal reference region to measure longitudinal amyloid-β change with 18F-florbetaben PET. J Nucl Med 2017;58:1300–6.


156. Baker SL, Maass A, Jagust WJ. Considerations and code for partial volume correcting [18F]-AV-1451 tau PET data. Data Brief 2017;15:648–57.



157. Young CB, Landau SM, Harrison TM, Poston KL, Mormino EC, ADNI. Influence of common reference regions on regional tau patterns in cross-sectional and longitudinal [18F]-AV-1451 PET data. Neuroimage 2021;243:118553.


158. Schwarz CG, Therneau TM, Weigand SD, Gunter JL, Lowe VJ, Przybelski SA, et al. Selecting software pipelines for change in flortaucipir SUVR: balancing repeatability and group separation. Neuroimage 2021;238:118259.


159. Southekal S, Devous MD Sr, Kennedy I, Navitsky M, Lu M, Joshi AD, et al. Flortaucipir F 18 quantitation using parametric estimation of reference signal intensity. J Nucl Med 2018;59:944–51.


160. Fu JF, Lois C, Sanchez J, Becker JA, Rubinstein ZB, Thibault E, et al. Kinetic evaluation and assessment of longitudinal changes in reference region and extracerebral [18F]MK-6240 PET uptake. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2023;43:581–94.



161. Harrison TM, Ward TJ, Murphy A, Baker SL, Dominguez PA, Koeppe R, et al. Optimizing quantification of MK6240 tau PET in unimpaired older adults. Neuroimage 2023;265:119761.


162. Soret M, Bacharach SL, Buvat I. Partial-volume effect in PET tumor imaging. J Nucl Med 2007;48:932–45.


163. Pawlik D, Leuzy A, Strandberg O, Smith R. Compensating for choroid plexus based off-target signal in the hippocampus using 18F-flortaucipir PET. Neuroimage 2020;221:117193.


164. Wolters EE, Ossenkoppele R, Golla SS, Verfaillie SC, Timmers T, Visser D, et al. Hippocampal [18F]flortaucipir BPND corrected for possible spill-in of the choroid plexus retains strong clinico-pathological relationships. Neuroimage Clin 2020;25:102113.