 |
 |
- Search
| Precis Future Med > Volume 2(4); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Impairment of lymphatic drainage may result in the development of lymphedema, a life-long disorder that results in significant morbidity. However, although lymphedema is common, current treatments are palliative in nature aiming to decrease swelling and control symptoms rather than cure the underlying problem. However, as our understanding in lymphatic biology increases, recent translational studies have described strategies that induce lymphangiogenesis to correct the underlying pathologic problem. These strategies can be classified into three categories: Increase the prolymphangiogenic drive (exogenous vascular endothelial growth factor C [VEGF-C] protein administration or VEGF-C gene delivery); suppress inflammation and inhibit production of antilymphangiogenic molecules (tacrolimus topical administration or leukotriene B4 antagonism); or cell therapy. In this review, we will briefly discuss the mechanisms regulating lymphangiogenesis along with recent translational studies that adopt strategies to modulate these mechanisms. We consider these strategies as candidate therapeutic options that may be in the near future used for the clinical treatment of lymphedema.
The lymphatic system is responsible for maintaining the tissue fluid homeostasis by transporting interstitial fluid, macromolecules, and immune cells back to the intravascular space [1]. Impairment of the lymphatic system results in accumulation of interstitial fluid in the extracellular tissue and in extreme cases resulting in lymphedema. This condition can present either as a congenital or hereditary form (primary lymphedema) or as an acquired disorder (secondary lymphedema). The most common cause of lymphedema in developed countries is secondary lymphedema resulting from lymphatic injury during cancer treatment [1,2]. Breast cancer is the most common cause of secondary lymphedema since this disease is common and often treated with lymph node resection. In fact, it is estimated that more than one in five breast cancer survivors go on to develop lymphedema [3]. However, it is important to note that lymphedema also occurs frequently in patients treated for melanoma, sarcoma, or gynecological/urological cancers. World-wide, parasitic infections are the most common cause of secondary lymphedema in developing countries affecting more than 150 million individuals.
Lymphedema is a debilitating disease resulting in chronic swelling of the affected extremity, impaired limb function, limited mobility, recurrent infections, decreased quality of life, and psychological problems [2,4,5]. Current treatments of lymphedema consist primarily of physiotherapy and compression garments aiming to decrease fluid accumulation and delay disease progression. However, these treatments are palliative in nature and do not promote restoration of lymphatic function after injury [1,6]. Consequently, there is an increasing demand for strategies that may alter the pathogenesis of lymphedema and restore the lymphatic function.
The pathogenesis of lymphedema is complex and although lymphatic injury is the initiating event, additional pathologic changes including inflammation and fibrosis are necessary for the development of the disease. In some cases, collateral lymphatics regenerate and lymphatic function is maintained thus preventing development of lymphedema [1]. In other cases, however, if the extent of damage is beyond the capacity of functional lymphatic recovery then these secondary changes are initiated and lymphedema eventually develops. This process is modulated by patient specific factors such as obesity, history of radiation, infections, and genetic predispositions.
Because lymphatic injury is the initiating event in the development of secondary lymphedema, a large number of preclinical studies have explored treatments designed to induce lymphangiogenesis as a means of treating lymphedema [4]. Induction of lymphangiogenesis can occur by increasing the expression of prolymphangiogenic growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) receptor. Other recent studies have shown that collateral lymphangiogenesis can occur by inhibiting inflammatory reactions which in turn decrease the production of antilymphangiogenic molecules. In the current manuscript, we review the cellular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis and discuss translational studies using these techniques with the goal of developing novel future therapies for the treatment of lymphedema.
The lymphatic system is a blind-ended vascular structure which is lined with a single layer of lymphatic endothelial cells. Lymphatic endothelial cells are terminally differentiated cells that are distinct from blood endothelial cells. Mature lymphatic endothelial cells express transcription factor/master regulator Prox-1, cell surface receptors like VEGF receptor 3 (VEGFR-3), lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE-1) and podoplanin (also known as D2-40) which also serve as lymphatic endothelial markers [1].
Development of the lymphatic system in the embryonic period starts with the expression of Prox-1 in a subset of endothelial cells of the cardinal vein. Prox-1 expressing lymphatic endothelial cells migrate and establish the primary lymph sac, from which the peripheral lymphatic vasculatures are generated by centrifugal sprouting and then expand to establish the lymphatic network. As a result, the lymphatic system ultimately forms a blind-ended vascular structure forming a one-way conduit [1].
The lymphatic system is a microstructure specialized for the absorption and transportation of immune cells and interstitial fluid. In the lymphatic capillaries (i.e., superficial lymphatic system), the basement membrane of lymphatic endothelial cells is discontinuous and overlapping flaps are anchored simply by discontinuous button-like vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin junctions (buttons) that serve as entry sites of fluid and inflammatory cells. In contrast, the collecting lymphatic channels consist of lymphatic endothelial cells that display continuous zipper-like junctions (zippers) which tightly seal up the borders and therefore function as simple conduits [7,8]. Once the lymph is absorbed, it is transported from the lymphatic capillaries into the pre-collecting lymphatic vessels that have sparse mural pericytes such as smooth muscle cells. The pre-collectors drain into the collecting lymphatic vessels which have a smooth muscle layer, basement membrane, valves and continuous zipper-like junctions between lymphatic endothelial cells [9].
According to the anatomic distribution, the lymphatic system can be largely divided into extra-nodal lymphatic vessels and intra-nodal lymphatic vessels. Extra-nodal lymphatic vessels function are conduits to transport fluid centrally while lymph nodes (and therefore intra-nodal lymphatic vessels) function as filters receiving lymph from multiple afferent extra-nodal lymphatic vessels [10].
Extra-nodular and intra-nodular lymphatic vessels share many characteristics in common including responsiveness to lymphangiogenic signaling molecules. However, these lymphatic vessels also have significant differences. One major difference that deserves emphasis is the potential for new vessels to be formed by lymphangiogenic stimuli and the subsequent regression of these vessels when the inducing stimulus is removed. Inflammatory lymphangiogenesis of intranodal lymphatic vessels occurs rapidly but regresses after the inflammatory stimulus is removed. In contrast, newly formed extra-nodal lymphatic vessels tend to persist once they have formed [11-14]. These changes are not absolute; however, it is clear that differences exist between intra-nodal and extra-nodal lymphatics.
In healthy adults the lymphatic system is stable when homeostasis is maintained and lymphangiogenesis, or expansion of the lymphatic network occurs in response to a variety of circumstances including acute inflammation, tissue repair, and around some tumors [10,15].
Several signaling pathways have prolymphangiogenic effects. However, the vast majority of studies aiming to treat lymphedema in preclinical models have focused on the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signaling pathway. VEGF-C stimulation regulates lymphatic endothelial cell proliferation, differentiation, tubule formation, and migration [1,10]. Over-expression of VEGF-C in transgenic mice results in lymphangiogenesis and expansion of the superficial lymphatic system. These lymphatic vessels are functional and can induce physiologic changes such as decreasing the severity of acute skin inflammation and edema in response to inflammatory stimuli [16,17], suggesting that VEGF-C probably can be exploited as an ideal therapeutic target for lymphedema. Interestingly, treatment with anti-VEGFR-3 antibodies (mF4-31C1) that inhibit VEGF-C signaling failed to suppress lymphatic vessels that had been already induced by inflammatory stimuli [7]. Although such phenomenon may be context dependent, these observations indicate that newly formed lymphatic vessels may be stable and persistent.
VEGF-A is another growth factor that has potent prolymphangiogenic effects. However, VEGF-A, unlike VEGF-C works in a context dependent manner and in some cases it is unclear whether the effects of VEGF-A are direct or indirect [18,19]. VEGF-A also regulates lymphatic vessel remodeling, as mice overexpressing VEGF-A display enlarged lymphatic vessels [20]. Other signaling pathways such as tumor necrosis factor α [18,21], toll-like receptor signaling [22], COX-2, and prostaglandin E2 receptor signaling [23,24] also have shown to have prolymphangiogenic effects under certain conditions.
Signaling pathways that have antilymphangiogenic effects have also been discovered. Interferon γ (IFN-γ), a cytokine produced by a variety of cells including T-cells and in some cases macrophages has potent antilymphangiogenic effects by modulating the Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway. This cytokine is particularly important for post-inflammatory regression of the expanded intra-nodal lymphatic vessels [12]. Similarly, T helper type 2 (Th2) cytokines including interleukin 4 (IL-4), IL-13 [25], and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) [26-28] as well as other extracellular molecules (e.g., endostatin [29], and thrombospondin [30]) have also been shown to have potent antilymphangiogenic effects [31]. Leukotriene B4, an inflammatory mediator that has increased expression in lymphedematous tissues also has significant antilymphangiogenic effects; however, the effects of this molecule are bimodal promoting lymphangiogenesis at low concentrations and antilymphangiogenic effects at high concentrations [32].
Recent reports have suggested that lymphangiogenesis is regulated by a balance between prolymphangiogenic and antilymphatic mechanisms. B lymphocytes [33,34], CD11b macrophages [17,35], and fibroblast-type reticular stromal cells [36] are important sources of prolymphangiogenic molecules including VEGF-C and VEGF-A. In contrast, T-cells are a main source of Th1 and Th2 cytokines with potent antilymphangiogenic effects [12]. Thus, a variety of cells can activate diverse signaling pathways that have effects on lymphatic endothelial cells and the balance of which can regulate promote or impair lymphatic vessel regeneration [10,12,31]. Therefore, strategies that either enhances the prolymphangiogenic drive or attenuate the anti-lymphatic forces may be potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
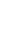
Current concepts in the pathophysiology of lymphedema suggest that treatments that preserve lymphatic function and improve collateral lymphatic formation may be effective treatments for this disease (Fig. 1). These approaches can be categorized as interventions that: (1) promote the prolymphangiogenic drive; (2) suppress inflammation and antilymphangiogenic mechanisms; and (3) provide the building blocks for lymphatic vessel regeneration (cell therapy).
Given the central role of VEGF-C in regulating lymphangiogenesis, many experiments have reported the use of recombinant VEGF-C or VEGF-C gene therapy for the treatment of lymphedema in preclinical models. In a study using the rabbit ear surgical model of lymphedema, a single injection of recombinant human VEGF-C protein at the site of lymphatic excision and along the neurovascular bundle successfully induced a marked lymphangiogenic response, increased drainage of interstitial fluid as assessed by radionucleotide lymphoscintigraphy, and decreased swelling and dermal thickness [37].
Gene therapy with recombinant viruses that express VEGF-C have also been reported. For example, delivery of VEGF-C using a recombinant adenovirus to a mouse model of primary lymphedema resulting from a heterozygous inactivating mutation in VEGFR3 gene (Chy mice) successfully induced the growth of functional lymphatic vessels in the skin [38].
Other studies have shown that VEGF-C gene therapy substantially increases the expression of VEGF-C locally, promotes a significant lymphangiogenic response, and decreased the severity of acute and chronic lymphedema in the rabbit ear and the mouse tail models of lymphedema [39]. Another study investigated the effects of VEGF-C or VEGF-D gene therapy with an adenovirus gene transfer vector following axillary lymph node dissection and reported that this treatment resulted in rapid and robust growth of lymphatic capillaries. Moreover, this treatment resulted in the regeneration of lymphatic vessels that underwent remodeling to resemble the collecting lymphatic vessels [40]. VE-cadherin and Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) expression in lymphatic vessels were discontinuous when examined 2 weeks after treatment while more uniform junctions were observed at 2 and 6 months. Two weeks after treatment, most of the newly generated lymphatic vessels had high levels of LYVE-1 expression indicating a lymphatic capillary phenotype. However, examination at 2 and 6 months demonstrated decreased expression of LYVE-1 in the newly formed lymphatic vessels. Finally, at 2 weeks most lymphatic vessels lacked smooth muscle cell coverage, but at 2 and 6 months most lymphatic vessels became partially covered by smooth muscle cells and developed lymphatic valves. [40]. Collectively, these results indicate that VEGF-C gene therapy is capable of not only inducing robust lymphangiogenesis, but also promoting maturation of the newly formed lymphatic vessels.
The basic rational for this strategy is derived from the fact that some inflammatory responses interfere with lymphatic repair and function in lymphedematous tissues. This concept is supported by the fact that recent studies have shown that the expression of lymphangiogenic growth factors such as VEGF-C are actually significantly increased in lymphedematous tissues and may, in fact play a role in increasing the severity of lymphedema by increasing fluid extravasation [43]. These findings suggest that antilymphangiogenic mechanisms actively oppose lymphatic regeneration and that this effect may play a more important pathologic role in lymphedema. Thus, inhibition of these responses can alter the balance of lymphatic repair and improve collateral lymphatic formation without increasing the expression of lymphangiogenic growth factors.
Tacrolimus is an U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved macrolide produced by the soil bacterium Streptomyces tsukubaensis that impairs T-cell differentiation and proliferation. The drug has been widely used to prevent rejection of transplanted organs and can also be used topically to treat cutaneous inflammatory/fibrotic diseases including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and localized scleroderma [44-46].
Topical administration of tacrolimus is effective in preventing and treating lymphedema in preclinical mouse lymphedema models resulting in a significant increase in collateral lymphatic formation, decreased inflammation, and decreased fibrosis [47]. The fact that tacrolimus is delivered topically is important since this mode of delivery can decrease the potential for systemic toxicity resulting from immunosuppression or renal injury.
Interestingly, the study demonstrated that formation of collateral lymphatics occurred without concomitant increases in the expression of VEGF-A or VEGF-C. Instead, treatment with tacrolimus suppressed the production of antilymphangiogenic cytokines including TGF-β1, IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-13 [47] supporting the concept that suppressing antilymphangiogenic stimuli is a potent means of increasing lymphangiogenesis and increasing lymphatic function.
Th2 cytokines (IL-4 and IL-13) have potent in vivo and in vitro antilymphangiogenic effects [25,48]. Recombinant IL-4 or IL-13 significantly decreased lymphatic endothelial cell proliferation, differentiation, and tubule formation in vitro. In contrast, blockade of Th2 cytokine function significantly increased inflammatory lymphangiogenesis in a corneal lymphangiogenesis model. Consistent with these findings, the authors demonstrated that inhibition of IL-4 or IL-13 with neutralizing antibodies prevents the initiation and progression of lymphedema in a mouse tail model. This treatment significantly decreased fibrosis, decreased edema and fat deposition, and increased lymphatic function without altering the expression of prolymphangiogenic growth factors [49]. Even if IL-4 neutralization was started 3 weeks after surgery at a period when lymphedema had been already established, tissue inflammation, fibrosis and lymphedema still markedly decreased while the lymphatic function markedly improved [49]. Interestingly, the expression of VEGF-A or VEGF-C did not increase indicating that Th2 cytokine inhibition improved the lymphatic function in a lymphangiogenic growth factor independent manner [49].
One research group reported that ketoprofen (an nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug inhibitor of cyclooxygenase) and a more narrowly targeted agent bestatin (leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitor) can induce treatment effect on lymphedema in a mouse model [32,50]. Leukotriene B4 was reported to have a bimodal, concentration-dependent effect and that high concentrations of leukotriene B4 interfered with lymphatic vessel repair [32]. In a mouse lymphedema model leukotriene B4 antagonism was sufficient to effectively reverse edema and restore the lymphatic architecture and function [32].
Post-natal lymphangiogenesis is known as a process that expand lymphatic networks through proliferation and migration of pre-existing lymphatic endothelial cells. But it has been recently reported that under certain circumstances, circulating progenitor cells may become incorporated into the growing lymphatic vessels and directly transdifferentiate into lymphatic endothelial cells (lymphovasculogenesis) even at the post-natal period [1,51]. This implies that supplements of therapeutic cells may promote the growth of lymphatic vessels if they can function as lymphatic endothelial cell precursors.
Compared with progenitor cells, embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have great pluripotentiality and proliferative capacity. Indeed, ESC and iPSC are attractive sources of therapeutic cells for regenerative medicine [52].
VEGFR-2 positive cells derived from ESC can successfully differentiate into lymphatic endothelial cells by the stimulation of VEGF-C and angiopoietin 1 [52,53]. Similarly, induced pluripotent stem (iPS) derived endothelial cells purified based on CD31 expression showed a marked increase in LYVE-1 and podoplanin expression when supplemented with VEGF-C and angiopoietin 1 during culture, indicating successful lymphatic differentiation [52,54]. These observations support the notion that ESC and iPSC can serve as a source of therapeutic cells that can be used for lymphatic vessel regeneration.
However, several issues must be considered prior to designing ESC or iPSC based cell therapies. The transplanted ESCs or iPSCs can potentially give rise to tumors (teratomas) and is a risk that cannot be neglected. In addition, ESCs can elicit immune responses and immunosuppressive treatment is necessary to prevent rejection. This treatment may increase the risk of complications such as wound healing, infection, tumor formation, and drug-associated toxicity [52]. Using iPSC may avoid these complications; however, this treatment may be complicated by the risk of viral integration into host chromosome thus causing a host of other potential problems [52].
Non-hematopoietic origin mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) such as bone marrow derived MSCs and adipose-derived stem cell (ASC) can serve as a source of lymphatic endothelial cells [52]. The treatment of lymphatic endothelial cell supernatant or purified recombinant VEGF-C to murine bone marrow derived MSC and human peripheral blood-derived MSCs induced up regulation of Prox-1 mRNA level as well as enhanced surface expression of podoplanin, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3, indicating that these cells have acquired lymphatic characteristics [55]. A mouse tail lymphedema model which was injected with this MSC not only demonstrated the regeneration of LYVE-1 and podoplanin positive lymphatic vessels, but also improvement of edema and restoration of lymphatic drainage [55].
In addition to bone marrow derived MSCs, ASCs are considered as a potential source of stem cells that may be ideal for lymphatic regeneration therapy. When stimulated with VEGF-C, ASC expressed a significant level of Prox-1, VEGF-C, and VEGF-A, whereas the expression of stem cell markers decreased [52,56]. Moreover, it has been suggested that ASC can induce lymphangiogenesis not only through direct differentiation but also by a paracrine factor-mediated manner [52]. ASC can produce various lymphangiogenic factors including VEGF-C and the conditioned medium from ASC culture has been reported to be capable of inducing lymphatic endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation [52,57].
In a study using a mouse hind limb lymphedema model, local transplantation of ASC successfully induced lymphangiogenesis [58]. This study suggested that the amplitude of regeneration was somewhat dependent on the number of ASCs delivered. Thus, while transplantation of 1× 104 ASC resulted in the regeneration of only capillary lymphatic vessels, transplantation of 1× 106 ASC resulted in the regeneration of the collecting lymphatic vessels suggesting that this treatment may be effective in regenerating the entire lymphatic tree [58].
One study further refined the MSC cell therapy by delivering the cells in a gelatin hydrogel containing VEGF-C in the form of a 3D scaffold matrix to support human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSC) and cultivate a microenvironment for differentiation. They demonstrated that the gelatin hydrogel scaffold maintained sustained release of VEGF-C for 4 weeks. Co-application hADSC and VEGF-C containing gelatin hydrogel achieved superior treatment efficacy of a mouse hindlimb lymphedema model compared to that of administrating either hADSCs or VEGF-C containing hydrogel alone [59].
Various investigative methods have adopted different strategies to enhance lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic function in order to rebuild the damaged lymphatic system and therefore eventually cure lymphedema. Accumulating evidence indicates that various methods to modulate the lymphatic system are available, and that at least in animal models these are successful in treating lymphedema. However, human have much more complex and vast lymphatic systems and it is unclear whether the encouraging results observed in these translational studies will be reproducible in the treatment of lymphedema patients. It is clear that extensive validation in safety issues and technical aspects are mandatory before these investigative methods can be applied to human patients, but hopefully they will expand our treatment options and ultimately cure lymphedema.
Each strategy has its own advantages and drawbacks. Administrating exogenous recombinant VEGF-C probably is the most simple and straightforward approach. But, the biological half-life and durability of recombinant protein is limited [52]. In addition, VEGF-C is known to promote tumor growth and metastasis [60] therefore delivery of large doses of this cytokine to a patient with a history of cancer may be problematic. VEGF-C gene therapy is even more problematic in this regard since VEGF-C expression is maintained for a longer period of time and there is a risk of systemic spillage of virus along with unexpected potential morbidities associated with chromosomal integration of viral genes [52]. ESC and iPS induced lymphatic endothelial progenitor cells have demonstrated many advantages for investigative cell therapy, but several substantial hurdles remain. Of note, the risk of potential teratoma formation originating from the transplanted stem cells is particularly problematic [52]. Meanwhile, MSC/ASC transplantation seems to be more practical for human application in a few aspects. (1) MSCs are easily isolated and expanded enabling autologous transplantation; (2) MSCs do not have a significant risk of malignant transformation [52,61]; (3) MSCs may act via diverse mechanisms to improve lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic repair.
The anti-lymphatic regulatory mechanism by T lymphocytes has been recently discovered [12], and recent studies have focused to induce lymphangiogenesis based on a strategy of suppressing the anti-lymphatic drive. For example, topical tacrolimus administration can effectively induce lymphangiogenesis and resolved lymphedema in mouse models [47]. Of note, tacrolimus is already used in clinically as a topical agent to treat dermatologic diseases [44-46] and as a systemic agent in patients who receive organ transplantation to prevent graft rejection [62,63].
In conclusion, translational studies provide accumulating evidence that experimental methods to expand the lymphatic system and improve lymphatic function may be promising strategies for treating lymphedema. Although further validation is necessary before these investigative methods can be applied clinically, we believe that they can expand our treatment options and possibly even cure lymphedema in the future.
Fig. 1.
Schematic drawing of investigative strategies for treating lymphedema which reset the balance between prolymphangiogenic drive and suppress inflammation and/or antilymphangiogenic drive to expand the lymphatic system. VEGF-C, exogenous vascular endothelial growth factor C; IFN-γ, interferon γ; IL, interleukin; LT B4, leukotriene B4.

REFERENCES
1. Tammela T, Alitalo K. Lymphangiogenesis: molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell 2010;140:460–76.


2. Soran A, D’Angelo G, Begovic M, Ardic F, Harlak A, Samuel Wieand H, et al. Breast cancer-related lymphedema: what are the significant predictors and how they affect the severity of lymphedema? Breast J 2006;12:536–43.


3. DiSipio T, Rye S, Newman B, Hayes S. Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 2013;14:500–15.


4. Baker A, Kim H, Semple JL, Dumont D, Shoichet M, Tobbia D, et al. Experimental assessment of pro-lymphangiogenic growth factors in the treatment of post-surgical lymphedema following lymphadenectomy. Breast Cancer Res 2010;12:R70.




5. Hayes SC, Johansson K, Stout NL, Prosnitz R, Armer JM, Gabram S, et al. Upper-body morbidity after breast cancer: incidence and evidence for evaluation, prevention, and management within a prospective surveillance model of care. Cancer 2012;118(8 Suppl):2237–49.


6. Cormier JN, Rourke L, Crosby M, Chang D, Armer J. The surgical treatment of lymphedema: a systematic review of the contemporary literature (2004-2010). Ann Surg Oncol 2012;19:642–51.


7. Baluk P, Fuxe J, Hashizume H, Romano T, Lashnits E, Butz S, et al. Functionally specialized junctions between endothelial cells of lymphatic vessels. J Exp Med 2007;204:2349–62.



8. Pflicke H, Sixt M. Preformed portals facilitate dendritic cell entry into afferent lymphatic vessels. J Exp Med 2009;206:2925–35.



10. Kim H, Kataru RP, Koh GY. Regulation and implications of inflammatory lymphangiogenesis. Trends Immunol 2012;33:350–6.


11. Baluk P, Tammela T, Ator E, Lyubynska N, Achen MG, Hicklin DJ, et al. Pathogenesis of persistent lymphatic vessel hyperplasia in chronic airway inflammation. J Clin Invest 2005;115:247–57.



12. Kataru RP, Kim H, Jang C, Choi DK, Koh BI, Kim M, et al. T lymphocytes negatively regulate lymph node lymphatic vessel formation. Immunity 2011;34:96–107.


13. Mumprecht V, Roudnicky F, Detmar M. Inflammation-induced lymph node lymphangiogenesis is reversible. Am J Pathol 2012;180:874–9.



14. Yao LC, Baluk P, Feng J, McDonald DM. Steroid-resistant lymphatic remodeling in chronically inflamed mouse airways. Am J Pathol 2010;176:1525–41.



15. Paupert J, Sounni NE, Noel A. Lymphangiogenesis in post-natal tissue remodeling: lymphatic endothelial cell connection with its environment. Mol Aspects Med 2011;32:146–58.


16. Huggenberger R, Siddiqui SS, Brander D, Ullmann S, Zimmermann K, Antsiferova M, et al. An important role of lymphatic vessel activation in limiting acute inflammation. Blood 2011;117:4667–78.



17. Kataru RP, Jung K, Jang C, Yang H, Schwendener RA, Baik JE, et al. Critical role of CD11b+ macrophages and VEGF in inflammatory lymphangiogenesis, antigen clearance, and inflammation resolution. Blood 2009;113:5650–9.


18. Guo R, Zhou Q, Proulx ST, Wood R, Ji RC, Ritchlin CT, et al. Inhibition of lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic drainage via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 blockade increases the severity of inflammation in a mouse model of chronic inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2009;60:2666–76.



19. Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV. Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature 2005;438:946–53.



20. Kunstfeld R, Hirakawa S, Hong YK, Schacht V, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Velasco P, et al. Induction of cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions in VEGF-A transgenic mice results in chronic skin inflammation associated with persistent lymphatic hyperplasia. Blood 2004;104:1048–57.


21. Zhu M, Fu YX. The role of core TNF/LIGHT family members in lymph node homeostasis and remodeling. Immunol Rev 2011;244:75–84.


22. Babu S, Anuradha R, Kumar NP, George PJ, Kumaraswami V, Nutman TB. Toll-like receptor- and filarial antigen-mediated, mitogen-activated protein kinase- and NF-κB-dependent regulation of angiogenic growth factors in filarial lymphatic pathology. Infect Immun 2012;80:2509–18.



23. Hosono K, Suzuki T, Tamaki H, Sakagami H, Hayashi I, Narumiya S, et al. Roles of prostaglandin E2-EP3/EP4 receptor signaling in the enhancement of lymphangiogenesis during fibroblast growth factor-2-induced granulation formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2011;31:1049–58.


24. Kashiwagi S, Hosono K, Suzuki T, Takeda A, Uchinuma E, Majima M. Role of COX-2 in lymphangiogenesis and restoration of lymphatic flow in secondary lymphedema. Lab Invest 2011;91:1314–25.



25. Shin K, Kataru RP, Park HJ, Kwon BI, Kim TW, Hong YK, et al. TH2 cells and their cytokines regulate formation and function of lymphatic vessels. Nat Commun 2015;6:6196.



26. Oka M, Iwata C, Suzuki HI, Kiyono K, Morishita Y, Watabe T, et al. Inhibition of endogenous TGF-beta signaling enhances lymphangiogenesis. Blood 2008;111:4571–9.


27. Clavin NW, Avraham T, Fernandez J, Daluvoy SV, Soares MA, Chaudhry A, et al. TGF-beta1 is a negative regulator of lymphatic regeneration during wound repair. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2008;295:H2113–27.


28. Avraham T, Daluvoy S, Zampell J, Yan A, Haviv YS, Rockson SG, et al. Blockade of transforming growth factor-beta1 accelerates lymphatic regeneration during wound repair. Am J Pathol 2010;177:3202–14.



29. Ou J, Li J, Pan F, Xie G, Zhou Q, Huang H, et al. Endostatin suppresses colorectal tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis by inhibiting expression of fibronectin extra domain A and integrin α9. J Cell Biochem 2011;112:2106–14.


30. Cursiefen C, Maruyama K, Bock F, Saban D, Sadrai Z, Lawler J, et al. Thrombospondin 1 inhibits inflammatory lymphangiogenesis by CD36 ligation on monocytes. J Exp Med 2011;208:1083–92.



31. Zampell JC, Avraham T, Yoder N, Fort N, Yan A, Weitman ES, et al. Lymphatic function is regulated by a coordinated expression of lymphangiogenic and anti-lymphangiogenic cytokines. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2012;302:C392–404.


32. Tian W, Rockson SG, Jiang X, Kim J, Begaye A, Shuffle EM, et al. Leukotriene B4 antagonism ameliorates experimental lymphedema. Sci Transl Med 2017;9:eaal3920.


33. Angeli V, Ginhoux F, Llodra J, Quemeneur L, Frenette PS, Skobe M, et al. B cell-driven lymphangiogenesis in inflamed lymph nodes enhances dendritic cell mobilization. Immunity 2006;24:203–15.


34. Shrestha B, Hashiguchi T, Ito T, Miura N, Takenouchi K, Oyama Y, et al. B cell-derived vascular endothelial growth factor A promotes lymphangiogenesis and high endothelial venule expansion in lymph nodes. J Immunol 2010;184:4819–26.


35. Kim KE, Koh YJ, Jeon BH, Jang C, Han J, Kataru RP, et al. Role of CD11b+ macrophages in intraperitoneal lipopolysaccharide-induced aberrant lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic function in the diaphragm. Am J Pathol 2009;175:1733–45.



36. Chyou S, Ekland EH, Carpenter AC, Tzeng TC, Tian S, Michaud M, et al. Fibroblast-type reticular stromal cells regulate the lymph node vasculature. J Immunol 2008;181:3887–96.



37. Szuba A, Skobe M, Karkkainen MJ, Shin WS, Beynet DP, Rockson NB, et al. Therapeutic lymphangiogenesis with human recombinant VEGF-C. FASEB J 2002;16:1985–7.


38. Karkkainen MJ, Saaristo A, Jussila L, Karila KA, Lawrence EC, Pajusola K, et al. A model for gene therapy of human hereditary lymphedema. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001;98:12677–82.



39. Yoon YS, Murayama T, Gravereaux E, Tkebuchava T, Silver M, Curry C, et al. VEGF-C gene therapy augments postnatal lymphangiogenesis and ameliorates secondary lymphedema. J Clin Invest 2003;111:717–25.



40. Tammela T, Saaristo A, Holopainen T, Lyytikka J, Kotronen A, Pitkonen M, et al. Therapeutic differentiation and maturation of lymphatic vessels after lymph node dissection and transplantation. Nat Med 2007;13:1458–66.



41. Tervala TV, Hartiala P, Tammela T, Visuri MT, Yla-Herttuala S, Alitalo K, et al. Growth factor therapy and lymph node graft for lymphedema. J Surg Res 2015;196:200–7.


42. Visuri MT, Honkonen KM, Hartiala P, Tervala TV, Halonen PJ, Junkkari H, et al. VEGF-C and VEGF-C156S in the prolymphangiogenic growth factor therapy of lymphedema: a large animal study. Angiogenesis 2015;18:313–26.


43. Gousopoulos E, Proulx ST, Bachmann SB, Dieterich LC, Scholl J, Karaman S, et al. An important role of VEGF-C in promoting lymphedema development. J Invest Dermatol 2017;137:1995–2004.


44. Mancuso G, Berdondini RM. Localized scleroderma: response to occlusive treatment with tacrolimus ointment. Br J Dermatol 2005;152:180–2.


45. Ruzicka T, Bieber T, Schopf E, Rubins A, Dobozy A, Bos JD, et al. A short-term trial of tacrolimus ointment for atopic dermatitis. European Tacrolimus Multicenter Atopic Dermatitis Study Group. N Engl J Med 1997;337:816–21.


46. Wang C, Lin A. Efficacy of topical calcineurin inhibitors in psoriasis. J Cutan Med Surg 2014;18:8–14.


47. Gardenier JC, Kataru RP, Hespe GE, Savetsky IL, Torrisi JS, Nores GD, et al. Topical tacrolimus for the treatment of secondary lymphedema. Nat Commun 2017;8:14345.



48. Savetsky IL, Ghanta S, Gardenier JC, Torrisi JS, Garcia Nores GD, Hespe GE, et al. Th2 cytokines inhibit lymphangiogenesis. PLoS One 2015;10:e0126908.



49. Avraham T, Zampell JC, Yan A, Elhadad S, Weitman ES, Rockson SG, et al. Th2 differentiation is necessary for soft tissue fibrosis and lymphatic dysfunction resulting from lymphedema. FASEB J 2013;27:1114–26.



50. Nakamura K, Radhakrishnan K, Wong YM, Rockson SG. Anti-inflammatory pharmacotherapy with ketoprofen ameliorates experimental lymphatic vascular insufficiency in mice. PLoS One 2009;4:e8380.



51. Kim H, Kataru RP, Koh GY. Inflammation-associated lymphangiogenesis: a double-edged sword? J Clin Invest 2014;124:936–42.



52. Qi S, Pan J. Cell-based therapy for therapeutic lymphangiogenesis. Stem Cells Dev 2015;24:271–83.


53. Kono T, Kubo H, Shimazu C, Ueda Y, Takahashi M, Yanagi K, et al. Differentiation of lymphatic endothelial cells from embryonic stem cells on OP9 stromal cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006;26:2070–6.


54. Rufaihah AJ, Huang NF, Kim J, Herold J, Volz KS, Park TS, et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells exhibit functional heterogeneity. Am J Transl Res 2013;5:21–35.


55. Conrad C, Niess H, Huss R, Huber S, von Luettichau I, Nelson PJ, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells acquire a lymphendothelial phenotype and enhance lymphatic regeneration in vivo. Circulation 2009;119:281–9.


56. Yan A, Avraham T, Zampell JC, Haviv YS, Weitman E, Mehrara BJ. Adipose-derived stem cells promote lymphangiogenesis in response to VEGF-C stimulation or TGF-β1 inhibition. Future Oncol 2011;7:1457–73.



57. Takeda K, Sowa Y, Nishino K, Itoh K, Fushiki S. Adipose-derived stem cells promote proliferation, migration, and tube formation of lymphatic endothelial cells in vitro by secreting lymphangiogenic factors. Ann Plast Surg 2015;74:728–36.


58. Yoshida S, Hamuy R, Hamada Y, Yoshimoto H, Hirano A, Akita S. Adipose-derived stem cell transplantation for therapeutic lymphangiogenesis in a mouse secondary lymphedema model. Regen Med 2015;10:549–62.


59. Hwang JH, Kim IG, Lee JY, Piao S, Lee DS, Lee TS, et al. Therapeutic lymphangiogenesis using stem cell and VEGF-C hydrogel. Biomaterials 2011;32:4415–23.


60. Karpanen T, Egeblad M, Karkkainen MJ, Kubo H, Yla-Herttuala S, Jaattela M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C promotes tumor lymphangiogenesis and intralymphatic tumor growth. Cancer Res 2001;61:1786–90.

61. Bernardo ME, Zaffaroni N, Novara F, Cometa AM, Avanzini MA, Moretta A, et al. Human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells do not undergo transformation after long-term in vitro culture and do not exhibit telomere maintenance mechanisms. Cancer Res 2007;67:9142–9.